> 作者:დ旧言~
> 座右铭:松树千年终是朽,槿花一日自为荣。
> 目标:手撕哈希表的闭散列和开散列
> 毒鸡汤:谁不是一边受伤,一边学会坚强。
> 专栏选自:C嘎嘎进阶
> 望小伙伴们点赞👍收藏✨加关注哟💕💕

🌟前言
我们已经模拟实现了哈希表,当然需要用哈希表来封装相关容器,最初的map和set封装是用红黑树,所以我们就不再封装了map和set,来封装它们的同胞兄弟unordered_map与unordered_set。对比前面map和set的封装还是比较简单的,咱们走起吧!!!
⭐主体
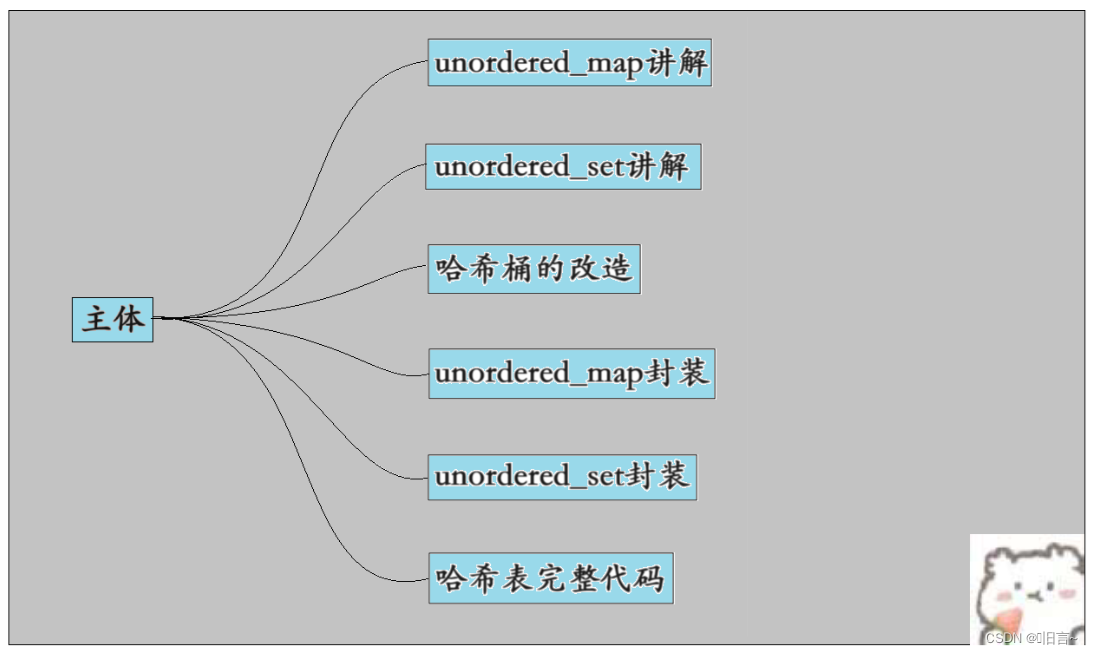
学习开散列实现unordered_map与unordered_set的封装咱们按照下面的图解:
🌙unordered_map讲解
概念:
unordered_map其实就是与map相对应的一个容器。学过map就知道,map的底层是一个红黑树,通过中序遍历的方式可以以有序的方式遍历整棵树。而unordered_map,正如它的名字一样,它的数据存储其实是无序的,这也和它底层所使用的哈希结构有关。而在其他功能上,unordered_map和map基本上就是一致的。
特点:
- unordered_map是用于存储键值对的关联式容器,它允许通过key快速的索引到对应的value。
- 在内部,unorder_map没有对按照任何特定的顺序排序,为了能在常数范围内找到key所对应的value,unordered_map将相同哈希值的键值对放在相同的桶中。
- unordered_map容器的搜索效率比map快,但它在遍历元素自己的范围迭代方面效率就比较低。
- 它的迭代器只能向前迭代,不支持反向迭代。
拓展:
从大结构上看,unordered_map和map的模板其实没有太大差距。学习了map和set我们就应该知道,map是通过T来告诉红黑树要构造的树的存储数据类型的,unordered_map也是一样的,但是它的参数中多了Hash和Pred两个参数,这两个参数都传了仿函数,主要和哈希结构有关。
使用:
统计水果个数:
int main() { string arr[] = { "西瓜","西瓜", "苹果", "梨", "苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "梨", "香蕉", "苹果", "西瓜" }; unordered_map count; for (auto& e : arr) { count[e]++; } for (auto e : count) { cout _next; } return end(); }💫删除函数
步骤:
在删除时,首先要调用hash函数获取关键码,根据对应位置上找。如果该位置存的数据为空,则表示不存在,返回;如果不为空,就比较键值,相同为找到,删除,不同就继续向下找直到为空。
注意:
哈希桶与哈希表不同,要删除数据时不能使用find()函数搜索。因为哈希桶中的数据是用单链表链接起来的,用find()就无法知道节点的父节点,进而无法链接链表。
代码:
// 删除函数 bool Erase(const K& key) { Hash hash; KeyOfT kot; size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size(); Node* prev = nullptr;//用于记录前一个节点 Node* cur = _tables[hashi]; while (cur) { if (kot(cur->_data) == key) { if (prev == nullptr)//要删除节点为头节点时 { _tables[hashi] = cur->_next; } else { prev->_next = cur->_next; } delete cur; return true; } else { prev = cur; cur = cur->_next; } } return false; }💫迭代器实现
步骤:
迭代器的结构体中首先要有哈希桶的指针。当然,迭代器的结构体中还需要有一个数据的指针,用于初始化迭代器,获取对应位置上的内容。
判断当前节点是否为空,不为空则返回;为空就说明当前下标对应的位置上已经没有数据了,就调用hash函数获取该节点的关键码。++关键码走向下一个下标,不为空则返回;为空则继续走,直到找到不为空的位置或结束。
图解:

注意:
哈希桶的begin()要返回的是第一个不为空的桶,而不是第一个节点
代码:
//迭代器 template struct __HashIterator { typedef HashNode Node; typedef HashTable HT; typedef __HashIterator Self; //定义一个普通迭代器 typedef __HashIterator Iterator; Node* _node; //节点的指针 HT* _ht; //哈希表 // 初始化列表 __HashIterator(Node* node, HT* ht) :_node(node), _ht(ht) {} // 初始化列表const __HashIterator(const Iterator& it) :_node(it._node), _ht(it._ht) {} Ref operator*() // 取值 { return _node->_data; } Ptr operator->() // 指向 { return &_node->_data; } bool operator!=(const Self& s) //使用节点的指针进行比较 { return _node != s._node; } //前置++ Self& operator++() { //若不处于当前桶的尾位置,则寻找桶的下一个位置 if (_node->_next != nullptr) { _node = _node->_next; } else { //若为空,则说明处于当前桶的尾位置,则需寻找下一个不为空的桶 KeyOfT kot; Hash hash; //计算当前桶位置 size_t hashi = hash(kot(_node->_data)) % _ht->_tables.size(); hashi++;//下一个位置 //寻找下一个不为空的桶 while (hashi _tables.size()) { if (_ht->_tables[hashi]) { _node = _ht->_tables[hashi]; break; } else { //桶为空,需要继续寻找 hashi++; } } //没有找到不为空的桶 if (hashi == _ht->_tables.size()) { _node = nullptr; } } return *this; } };💫友元声明
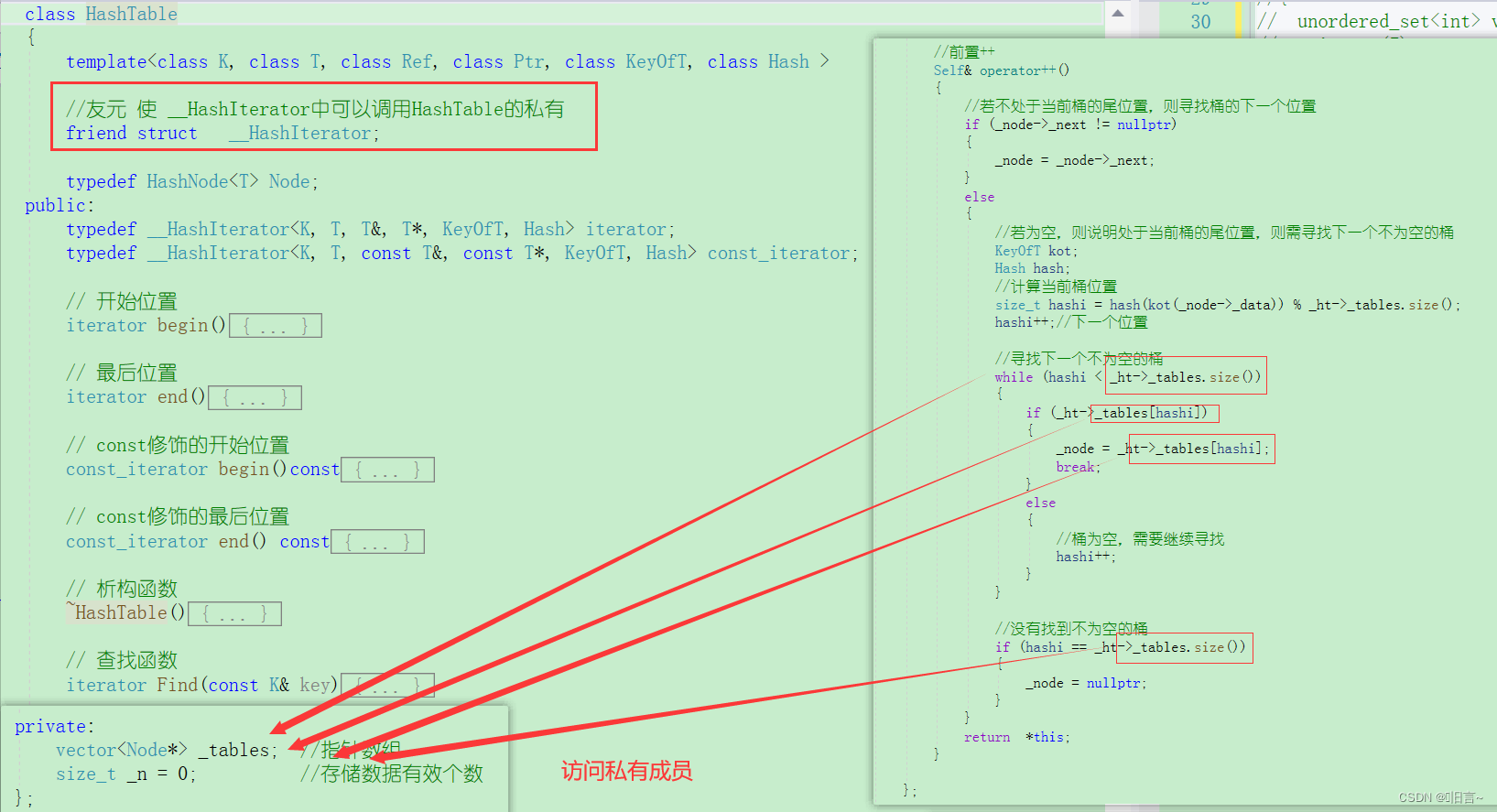
解析:
在++迭代器的时候,会使用到哈希表指针,哈希表指针又会使用到HashTable中的_tables。HashTable中的_tables是私有成员,在类外是不能访问的。解决这个问题可以在HashTable中写一个公有的访问函数,也可以采用友元。
图解:
🌙unordered_map封装
代码如下:
#include"HashTable.h" namespace lyk { template class unordered_map { // 仿函数 struct MapKeyOfT { const K& operator()(const pair& kv) { return kv.first; } }; public: typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable::iterator iterator; // 开始位置 iterator begin() { return _ht.begin(); } // 结束位置 iterator end() { return _ht.end(); } V& operator[](const K& key) { pair ret = insert(make_pair(key, V())); return ret->first->second; } // 插入函数 pair insert(const pair& kv) { return _ht.insert(kv); } // 查找函数 iterator find(const K& key) { return _ht.Find(); } // 删除函数 bool erase(const K& key) { return _ht.Erase(key); } private: hash_bucket::HashTable _ht; }; // 测试一 void test_map1() { unordered_map v; v.insert(make_pair(1, 1)); v.insert(make_pair(3, 3)); v.insert(make_pair(10, 10)); v.insert(make_pair(2, 2)); v.insert(make_pair(8, 8)); unordered_map::iterator it = v.begin(); while (it != v.end()) { cout first _data) == key) { return iterator(cur, this); } cur = cur->_next; } return end(); } // 删除函数 bool Erase(const K& key) { Hash hash; KeyOfT kot; size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size(); Node* prev = nullptr;//用于记录前一个节点 Node* cur = _tables[hashi]; while (cur) { if (kot(cur->_data) == key) { if (prev == nullptr)//要删除节点为头节点时 { _tables[hashi] = cur->_next; } else { prev->_next = cur->_next; } delete cur; return true; } else { prev = cur; cur = cur->_next; } } return false; } // 插入元素 pair insert(const T& data)//插入 { KeyOfT kot; //若对应的数据已经存在,则插入失败 iterator it = Find(kot(data)); if (it != end()) { return make_pair(it, false); } Hash hash; //负载因子==1时扩容 if (_n == _tables.size()) { size_t newsize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : _tables.size() * 2; // 创建 newsize个数据,每个数据都为空 vectornewtables(newsize, nullptr); for (auto& cur : _tables) { while (cur) { //保存下一个旧表节点 Node* next = cur->_next; size_t hashi = hash(kot(cur->_data)) % newtables.size(); //将旧表节点头插到新表节点中 cur->_next = newtables[hashi]; newtables[hashi] = cur; cur = next; } } _tables.swap(newtables); } size_t hashi = hash(kot(data)) % _tables.size(); //头插 Node* newnode = new Node(data);//新建节点 newnode->_next = _tables[hashi]; _tables[hashi] = newnode; ++_n; return make_pair(iterator(newnode, this), true); } private: vector _tables; //指针数组 size_t _n = 0; //存储数据有效个数 }; }🌟结束语
今天内容就到这里啦,时间过得很快,大家沉下心来好好学习,会有一定的收获的,大家多多坚持,嘻嘻,成功路上注定孤独,因为坚持的人不多。那请大家举起自己的小手给博主一键三连,有你们的支持是我最大的动力💞💞💞,回见。