大家好,我是 同学小张,持续学习C++进阶知识和AI大模型应用实战案例,持续分享,欢迎大家点赞+关注,共同学习和进步。
上篇文章我们详细学习了LATS方法的原理,本文我们以LangChain中实现的LATS代码入手,看看怎么真正用代码实现出LATS。
文章目录
- 0. 原理回顾
- 1. 代码详解
- 1.1 LangGraph的创建
- 1.2 状态state的实现
- 1.3 节点node的实现
- 1.3.1 start节点
- 1.3.1.1 初始化信息 initial_answer_chain
- 1.3.1.2 解析结果
- 1.3.1.3 执行工具获取执行工具结果 tool_executor
- 1.3.1.4 评估反思 reflection_chain
- 1.3.1.5 Reflection类
- 1.3.2 expand节点
- 1.3.2.1 选择 best_candidate
- 1.3.2.2 扩展 expansion_chain
- 1.3.2.3 评估+反思
- 1.3.2.4 扩展树和反向传播
- 1.4 执行
- 2. 总结
0. 原理回顾
这是LATS论文中的步骤图:
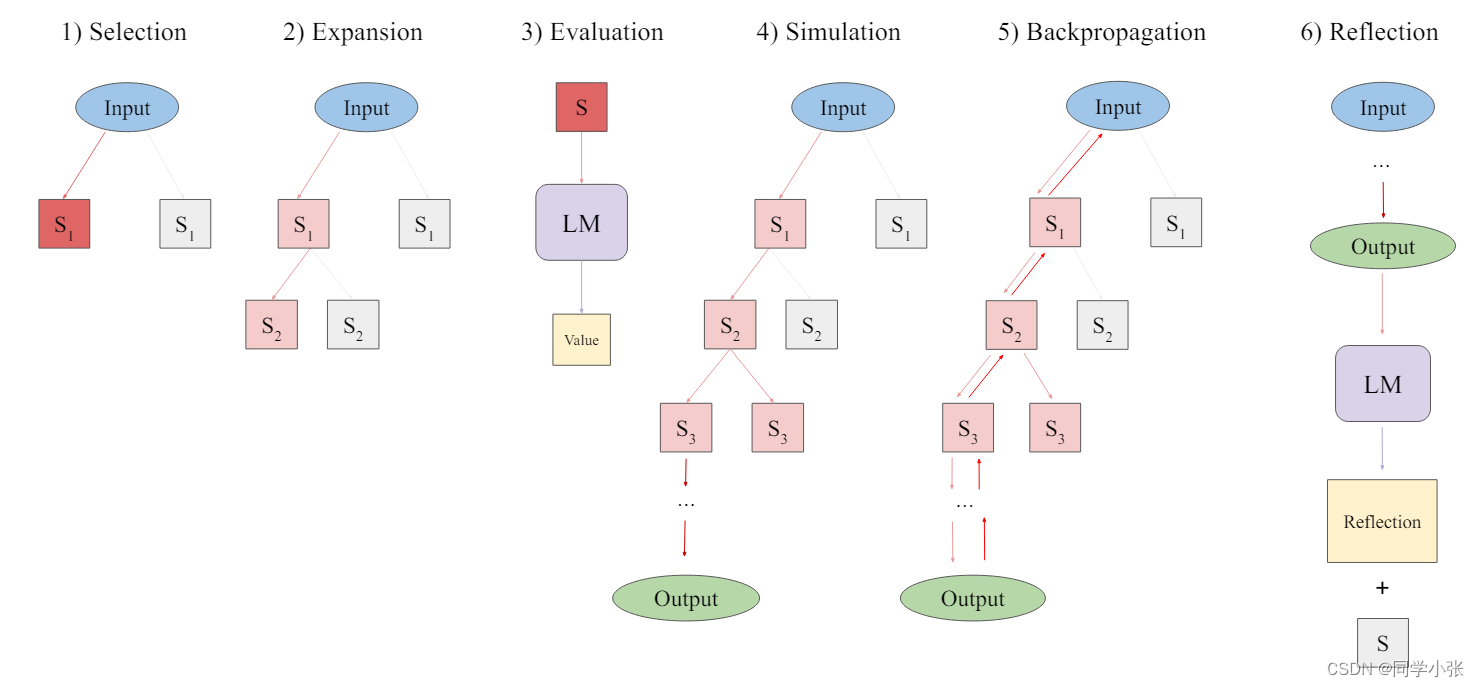
LATS的实现需要:选择、扩展、评估、模拟、反向传播和反思的过程。
LangChain中的代码实现步骤如下:
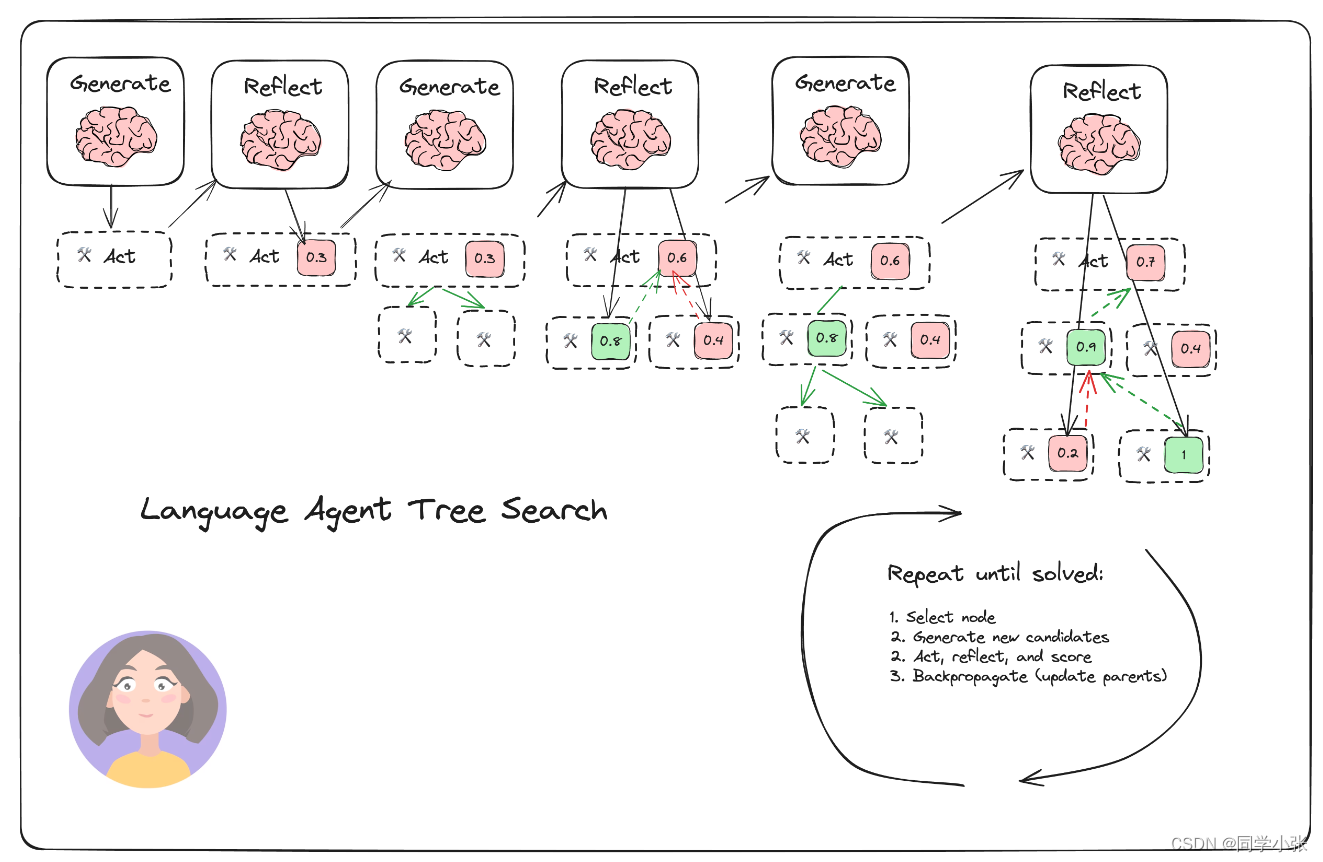
将步骤简化为:
(1)选择
(2)扩展
(3)评估 + 反思 + 模拟 + 打分
(4)反向传播
1. 代码详解
下面我们一起来看下它的源码实现。
完整代码参考:https://github.com/langchain-ai/langgraph/blob/main/examples/lats/lats.ipynb
1.1 LangGraph的创建
LangGraph的创建是一个非常标准的套路:
(1)创建LangGraph对象
builder = StateGraph(TreeState)
(2) 添加节点
builder.add_node("start", generate_initial_response) builder.add_node("expand", expand)(3)设置初始进入节点
builder.set_entry_point("start")(4)添加边,都是条件边
builder.add_conditional_edges( "start", # Either expand/rollout or finish should_loop, ) builder.add_conditional_edges( "expand", # Either continue to rollout or finish should_loop, )(5)编译图
graph = builder.compile()
这就定义好了一个LangGraph,图的执行路径是这样的:
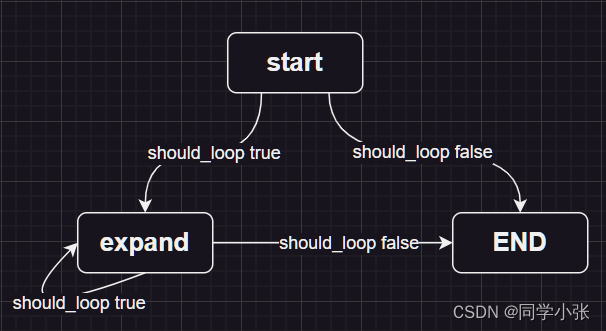
其中 should_loop 函数的定义:
def should_loop(state: TreeState): """Determine whether to continue the tree search.""" root = state["root"] if root.is_solved: return END if root.height > 5: return END return "expand"如果判定已经得到了最终答案(is_solved),或者搜索的最大层数超过了5层,则停止搜索答案,不再继续搜索。否则继续执行 expand 节点。
有了这个LangGraph的框架,我总结的LangGraph创建需要的三要素:节点node、边edge和状态state:边edge上面已经定义了,下面看下节点node和状态state的实现。
1.2 状态state的实现
from typing_extensions import TypedDict class TreeState(TypedDict): # The full tree root: Node # The original input input: str自定义的状态state为TreeState,里面有一个Node类型的root字段,和一个str类型的input字段。
1.3 节点node的实现
1.3.1 start节点
start节点是执行 generate_initial_response函数,构造根节点:
def generate_initial_response(state: TreeState) -> dict: """Generate the initial candidate response.""" res = initial_answer_chain.invoke({"input": state["input"]}) parsed = parser.invoke(res) tool_responses = tool_executor.batch( [ToolInvocation(tool=r["type"], tool_input=r["args"]) for r in parsed] ) output_messages = [res] + [ ToolMessage(content=json.dumps(resp), tool_call_id=tool_call["id"]) for resp, tool_call in zip(tool_responses, parsed) ] reflection = reflection_chain.invoke( {"input": state["input"], "candidate": output_messages} ) root = Node(output_messages, reflection=reflection) return { **state, "root": root, }1.3.1.1 初始化信息 initial_answer_chain
initial_answer_chain 代码如下:实现的功能是将用户提问输入给大模型,大模型给出回复。从Prompt看,基本就是个直来直去的问答。
prompt_template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages( [ ( "system", "You are an AI assistant.", ), ("user", "{input}"), MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="messages", optional=True), ] ) initial_answer_chain = prompt_template | llm.bind_tools(tools=tools).with_config( run_name="GenerateInitialCandidate" )1.3.1.2 解析结果
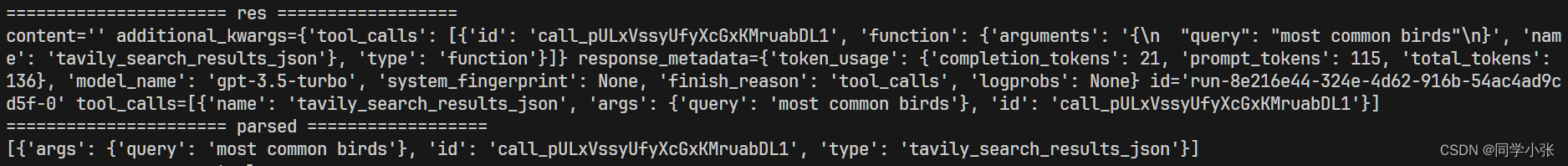
回复之后,使用Json解析器解析一下:
parser = JsonOutputToolsParser(return_id=True)
这两步的运行结果大体如下:
1.3.1.3 执行工具获取执行工具结果 tool_executor
tool_executor 将上一步解析出来的工具进行并行执行,并获取结果。下面是工具的定义:
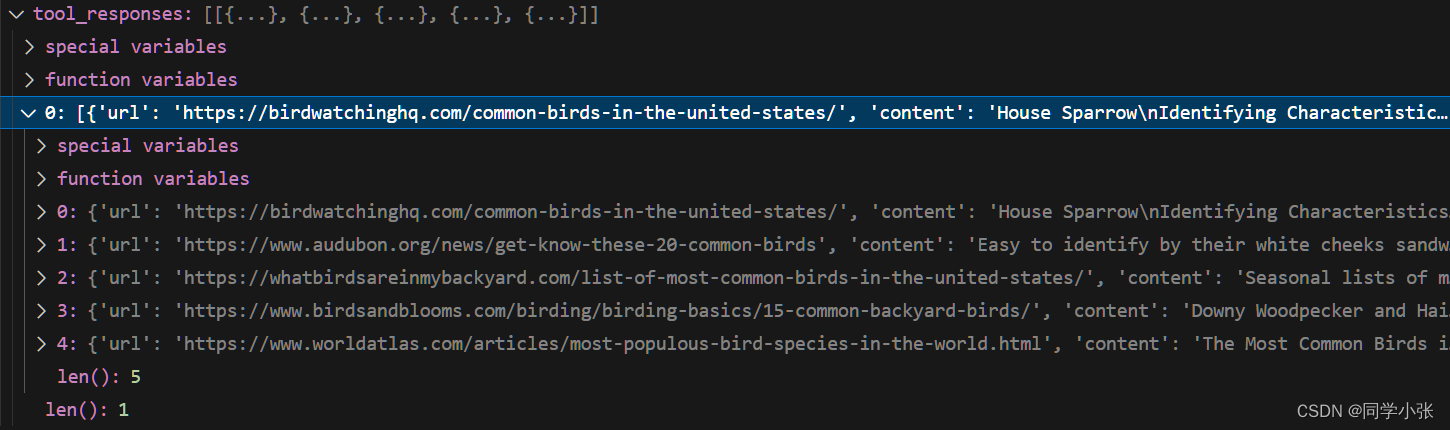
search = TavilySearchAPIWrapper() tavily_tool = TavilySearchResults(api_wrapper=search, max_results=5) tools = [tavily_tool] tool_executor = ToolExecutor(tools=tools)
执行完工具后结果类似如下:
1.3.1.4 评估反思 reflection_chain
reflection_chain 用来对工具执行结果进行打分评估。
@as_runnable def reflection_chain(inputs) -> Reflection: tool_choices = reflection_llm_chain.invoke(inputs) reflection = tool_choices[0] if not isinstance(inputs["candidate"][-1], AIMessage): reflection.found_solution = False return reflection其中的 reflection_llm_chain 定义如下:
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages( [ ( "system", "Reflect and grade the assistant response to the user question below.", ), ("user", "{input}"), MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="candidate"), ] ) reflection_llm_chain = ( prompt | llm.bind_tools(tools=[Reflection], tool_choice="Reflection").with_config( run_name="Reflection" ) | PydanticToolsParser(tools=[Reflection]) )从Prompt就大体能看出来,是利用大模型进行反思和打分。输入是用户的原始问题和候选的节点candidate。tool_choice="Reflection"强制让大模型使用 Reflection工具,最后将大模型返回结果使用 Reflection进行解析。
最终,该chain返回的结果是一个 Reflection实例。
Reflection 执行结果示例:包括一个说明、一个评分和是否是最终答案。参考 Reflection类的实现。

1.3.1.5 Reflection类
class Reflection(BaseModel): reflections: str = Field( description="The critique and reflections on the sufficiency, superfluency," " and general quality of the response" ) score: int = Field( description="Score from 0-10 on the quality of the candidate response.", gte=0, lte=10, ) found_solution: bool = Field( description="Whether the response has fully solved the question or task." ) def as_message(self): return HumanMessage( content=f"Reasoning: {self.reflections}\nScore: {self.score}" ) @property def normalized_score(self) -> float: return self.score / 10.0问题:这个Reflection类没有定义为tools,为什么能直接这样写: tools=[Reflection]?
1.3.2 expand节点
这个节点执行的就是整个LATS的流程:选择、扩展、评估、模拟、反向传播和反思。
def expand(state: TreeState, config: RunnableConfig) -> dict: """Starting from the "best" node in the tree, generate N candidates for the next step.""" root = state["root"] best_candidate: Node = root.best_child if root.children else root messages = best_candidate.get_trajectory() # Generate N candidates from the single child candidate new_candidates = expansion_chain.invoke( {"input": state["input"], "messages": messages}, config ) parsed = parser.batch(new_candidates) flattened = [ (i, tool_call) for i, tool_calls in enumerate(parsed) for tool_call in tool_calls ] tool_responses = tool_executor.batch( [ ToolInvocation(tool=tool_call["type"], tool_input=tool_call["args"]) for _, tool_call in flattened ] ) collected_responses = defaultdict(list) for (i, tool_call), resp in zip(flattened, tool_responses): collected_responses[i].append( ToolMessage(content=json.dumps(resp), tool_call_id=tool_call["id"]) ) output_messages = [] for i, candidate in enumerate(new_candidates): output_messages.append([candidate] + collected_responses[i]) # Reflect on each candidate # For tasks with external validation, you'd add that here. reflections = reflection_chain.batch( [{"input": state["input"], "candidate": msges} for msges in output_messages], config, ) # Grow tree child_nodes = [ Node(cand, parent=best_candidate, reflection=reflection) for cand, reflection in zip(output_messages, reflections) ] best_candidate.children.extend(child_nodes) # We have already extended the tree directly, so we just return the state return state1.3.2.1 选择 best_candidate
选择当前最优的节点。
以下代码从 best_child开始看,首先是获取树的全部节点和子孙节点。取分数最高的节点。
怎么取分数最高的节点?这里调用了 upper_confidence_bound函数。这个函数用来计算UCT分数,UCT 是一种常用于多臂赌博机问题(Multi-Armed Bandit Problem)和蒙特卡洛树搜索(Monte Carlo Tree Search, MCTS)的算法,它有助于在探索(exploration)和利用(exploitation)之间找到一个平衡。
def upper_confidence_bound(self, exploration_weight=1.0): """Return the UCT score. This helps balance exploration vs. exploitation of a branch.""" if self.parent is None: raise ValueError("Cannot obtain UCT from root node") if self.visits == 0: return self.value # Encourages exploitation of high-value trajectories average_reward = self.value / self.visits # Encourages exploration of less-visited trajectories exploration_term = math.sqrt(math.log(self.parent.visits) / self.visits) return average_reward + exploration_weight * exploration_term @property def best_child(self): """Select the child with the highest UCT to search next.""" if not self.children: return None all_nodes = self._get_all_children() return max(all_nodes, key=lambda child: child.upper_confidence_bound())1.3.2.2 扩展 expansion_chain
这一步是利用大模型,对于单个输入,生成N个不同的输出。prompt_template与前面初始化节点中的一致,基本是直来直去的问答,只是一次生成多个结果。
# This generates N candidate values for a single input to sample actions from the environment def generate_candidates(messages: ChatPromptValue, config: RunnableConfig): n = config["configurable"].get("N", 5) bound_kwargs = llm.bind_tools(tools=tools).kwargs chat_result = llm.generate( [messages.to_messages()], n=n, callbacks=config["callbacks"], run_name="GenerateCandidates", **bound_kwargs ) return [gen.message for gen in chat_result.generations[0]] expansion_chain = prompt_template | generate_candidates候选节点生成结果示例:
[AIMessage(content='', additional_kwargs={'tool_calls': [{'id': 'call_5DMq9O6BIden7lLraFH0NuYZ', 'function': {'arguments': '{"query":"lithium pollution research report"}', 'name': 'tavily_search_results_json'}, 'type': 'function'}]}), AIMessage(content='', additional_kwargs={'tool_calls': [{'id': 'call_5DMq9O6BIden7lLraFH0NuYZ', 'function': {'arguments': '{"query":"lithium pollution research report"}', 'name': 'tavily_search_results_json'}, 'type': 'function'}]}), AIMessage(content='', additional_kwargs={'tool_calls': [{'id': 'call_5DMq9O6BIden7lLraFH0NuYZ', 'function': {'arguments': '{"query":"lithium pollution research report"}', 'name': 'tavily_search_results_json'}, 'type': 'function'}]}), AIMessage(content='', additional_kwargs={'tool_calls': [{'id': 'call_5DMq9O6BIden7lLraFH0NuYZ', 'function': {'arguments': '{"query":"lithium pollution research report"}', 'name': 'tavily_search_results_json'}, 'type': 'function'}]}), AIMessage(content='', additional_kwargs={'tool_calls': [{'id': 'call_5DMq9O6BIden7lLraFH0NuYZ', 'function': {'arguments': '{"query":"lithium pollution research report"}', 'name': 'tavily_search_results_json'}, 'type': 'function'}]})]生成完N个候选节点之后,通过 解析结果、并行执行工具得到每个节点执行的结果。
1.3.2.3 评估+反思
对每个候选节点进行评估反思 reflection_chain
1.3.2.4 扩展树和反向传播
将新增的节点添加到树中
# Grow tree child_nodes = [ Node(cand, parent=best_candidate, reflection=reflection) for cand, reflection in zip(output_messages, reflections) ] best_candidate.children.extend(child_nodes)添加之后,树中已经有了这些子节点:
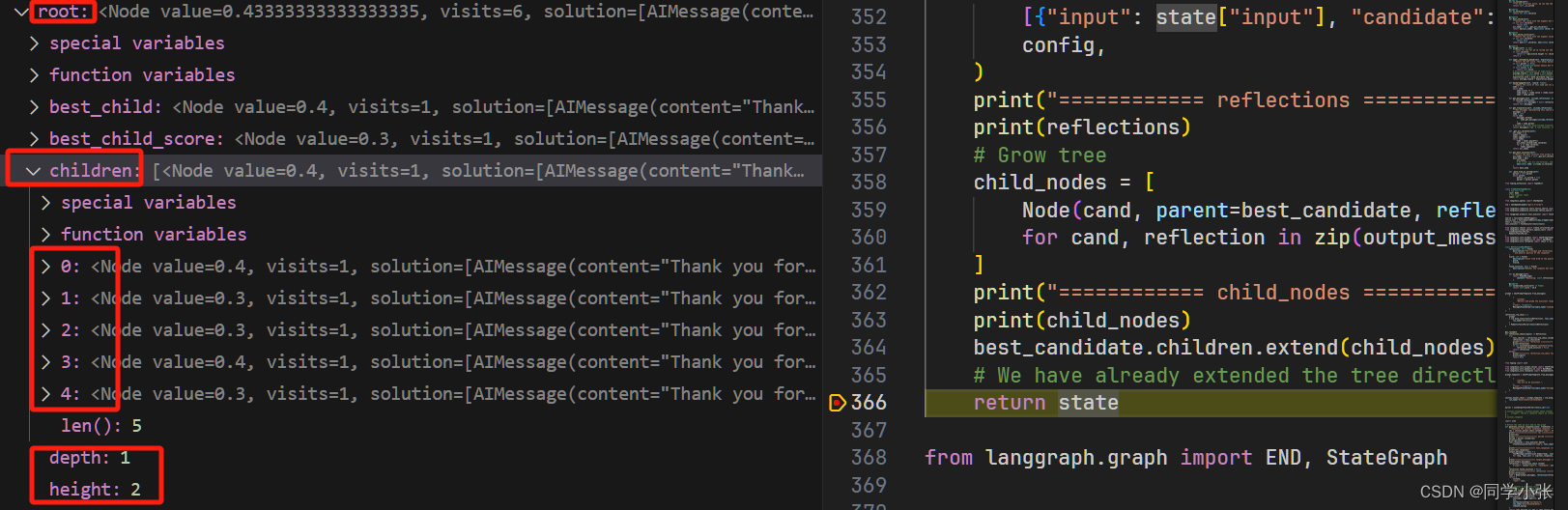
值得注意的是,这里面也包含了反向传播步骤。当新创建一个Node实例时,会调用反向传播:
class Node: def __init__( self, messages: List[BaseMessage], reflection: Reflection, parent: Optional[Node] = None, ): ...... self.backpropagate(reflection.normalized_score)反向传播的实际作用,就是更新这条路径上各个节点的分数:
def backpropagate(self, reward: float): """Update the score of this node and its parents.""" node = self while node: node.visits += 1 node.value = (node.value * (node.visits - 1) + reward) / node.visits node = node.parent1.4 执行
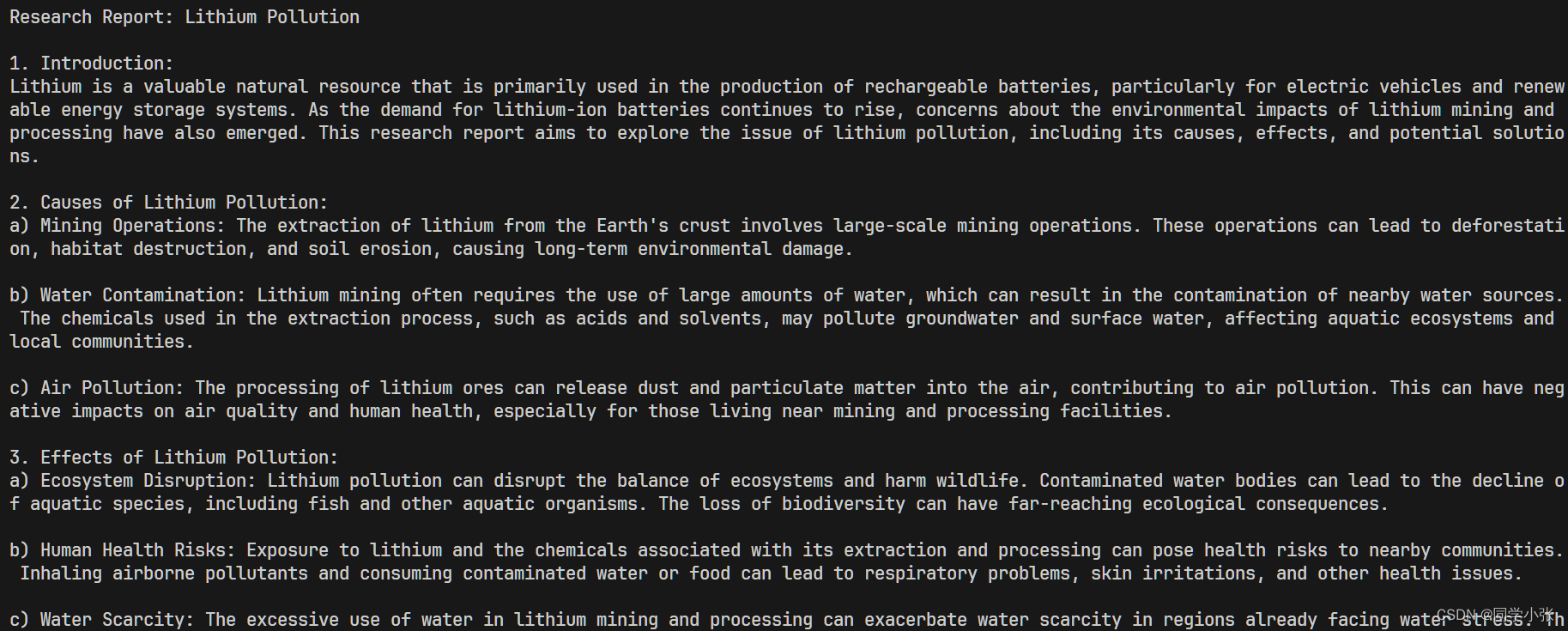
question = "Write a research report on lithium pollution." for step in graph.stream({"input": question}): step_name, step_state = next(iter(step.items())) print(step_name) print("rolled out: ", step_state["root"].height) print("---") # solution_node = step["__end__"]["root"].get_best_solution() ## 这一句我没运行成功,暂且不管吧 solution_node = step["start"]["root"].get_best_solution() best_trajectory = solution_node.get_trajectory(include_reflections=False) print(best_trajectory[-1].content)执行完之后最后输出结果是:最终节点的content。
best_trajectory = solution_node.get_trajectory(include_reflections=False) print(best_trajectory[-1].content)最终输出结果示例:
2. 总结
本文我们对LangChain中实现LATS的源码进行了详细的学习和拆解,希望能够帮助大家更好地理解LATS,给大家做一个参考。
LATS的六步:选择、扩展、评估、模拟、反向传播和反思。其中评估、模拟和反思可以合并在一起执行,模拟其实就是执行工具获取工具的执行结果,反向传播其实就是更新这条路径上各个节点的得分。
代码中细节很多,理解不到位的地方,欢迎大家批评指正。
如果觉得本文对你有帮助,麻烦点个赞和关注呗 ~~~
- 大家好,我是 同学小张,持续学习C++进阶知识和AI大模型应用实战案例
- 欢迎 点赞 + 关注 👏,持续学习,持续干货输出。
- +v: jasper_8017 一起交流💬,一起进步💪。
- 微信公众号也可搜【同学小张】 🙏
本站文章一览: