目录
action
ActionsGPT
ai-plugin.json
tool参数
计算加法
获取位置和查找位置,多fuction
配置函数功能
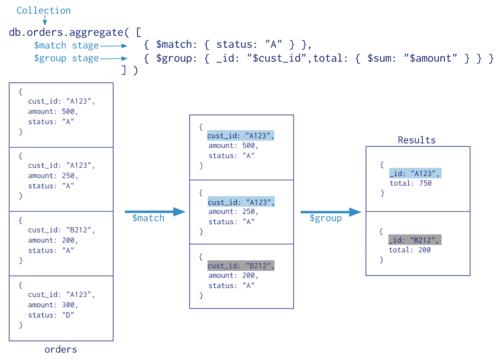
nl2sql
tool代码
函数
流式输出
代码
ChatGLM3-6B
NLP算法工程师视角:
action
这个功能非常强大,让GPT的使用方式变得更加多样化。通过Actions,我们可以访问各种API,比如天气查询和日历查询等。但今天,我要介绍的不只是这些小功能。 Zapier的官方介绍中提到,GPT的Zapier AI Actions可以让您在超过6,000个应用程序中进行超过20K次的搜索和操作,这赋予了GPT超能力。也就是说,这个功能非常强大,有很多种玩法!
ActionsGPT
第一次使用此功能,你需要转到“Create a GPT”部分。选择“Configure”-“Create new action”,然后你可以从 ActionsGPT 获得帮助。
点击“Keep in sidebar”将ActionsGPT保持在左侧,方便后续直接进入。
主要它的功能:
1. 解析curl命令:我可以从提供的cURL命令中提取信息,并根据这些信息创建一个OpenAPI规范。
2. 理解代码片段:如果你提供一个关于如何与一个URL交互的代码片段,我可以从中提炼出必要的信息,以创建一个对应的OpenAPI规范。
3. 处理API描述:即便没有具体的代码或命令,只要你能描述如何与一个API交互(比如HTTP方法、路径、请求和响应的结构等),我也能据此创建一个OpenAPI规范。
4. 浏览和解析在线API文档:如果有在线的API文档,我可以浏览这些文档来理解API的细节,并据此创建一个OpenAPI规范。
5. 创建和调整OpenAPI规范:我可以为每个API操作创建规范,包括operationId(操作ID,用于唯一标识每个操作),并确保规范的有效性。
6. 调试和修改规范:在创建规范后,如果需要进行调整或解决问题,我可以帮助修改和调试OpenAPI规范。
7. 提供详细说明:我会详细阐述创建的OpenAPI规范的每个部分,以帮助用户理解和使用它。
ai-plugin.json
"schema_version": "v1", //配置文件版本 "name_for_human": "Sport Stats", //插件名字,给用户看的名字 "name_for_model": "sportStats", //插件名字,给ChatGPT模型看的名字,需要唯一 "description_for_human": "Get current and historical stats for sport players and games.", //描述插件的功能,这个字段是在插件市场展示给用户看的 "description_for_model": "Get current and historical stats for sport players and games. Always display results using Markdown tables.", //描述插件的功能,ChatGPT会分析这个字段,确定什么时候调用你的插件 "auth": { "type": "none" //这个是API认证方式,none 代表不需要认证 }, "api": { "type": "openapi", "url": "PLUGIN_HOSTNAME/openapi.yaml" //这个是Swagger API文档地址,ChatGPT通过这个地址访问我们的api文档 }, "logo_url": "PLUGIN_HOSTNAME/logo.png", //插件logo地址 "contact_email": "support@example.com", //插件官方联系邮件 "legal_info_url": "https://example.com/legal" //与该插件相关的legal information
openapi.yaml
openapi: 3.0.1
info:
title: Sport Stats
description: Get current and historical stats for sport players and games.
version: "v1"
servers:
- url: PLUGIN_HOSTNAME
paths:
/players:
get:
operationId: getPlayers
summary: Retrieves all players from all seasons whose names match the query string.
parameters:
- in: query
name: query
schema:
type: string
description: Used to filter players based on their name. For example, ?query=davis will return players that have 'davis' in their first or last name.
responses:
"200":
description: OK
/teams:
get:
operationId: getTeams
summary: Retrieves all teams for the current season.
responses:
"200":
description: OK
/games:
get:
operationId: getGames
summary: Retrieves all games that match the filters specified by the args. Display results using markdown tables.
parameters:
- in: query
name: limit
schema:
type: string
description: The max number of results to return.
- in: query
name: seasons
schema:
type: array
items:
type: string
description: Filter by seasons. Seasons are represented by the year they began. For example, 2018 represents season 2018-2019.
- in: query
name: team_ids
schema:
type: array
items:
type: string
description: Filter by team ids. Team ids can be determined using the getTeams function.
- in: query
name: start_date
schema:
type: string
description: A single date in 'YYYY-MM-DD' format. This is used to select games that occur on or after this date.
- in: query
name: end_date
schema:
type: string
description: A single date in 'YYYY-MM-DD' format. This is used to select games that occur on or before this date.
responses:
"200":
description: OK
/stats:
get:
operationId: getStats
summary: Retrieves stats that match the filters specified by the args. Display results using markdown tables.
parameters:
- in: query
name: limit
schema:
type: string
description: The max number of results to return.
- in: query
name: player_ids
schema:
type: array
items:
type: string
description: Filter by player ids. Player ids can be determined using the getPlayers function.
- in: query
name: game_ids
schema:
type: array
items:
type: string
description: Filter by game ids. Game ids can be determined using the getGames function.
- in: query
name: start_date
schema:
type: string
description: A single date in 'YYYY-MM-DD' format. This is used to select games that occur on or after this date.
- in: query
name: end_date
schema:
type: string
description: A single date in 'YYYY-MM-DD' format. This is used to select games that occur on or before this date.
responses:
"200":
description: OK
/season_averages:
get:
operationId: getSeasonAverages
summary: Retrieves regular season averages for the given players. Display results using markdown tables.
parameters:
- in: query
name: season
schema:
type: string
description: Defaults to the current season. A season is represented by the year it began. For example, 2018 represents season 2018-2019.
- in: query
name: player_ids
schema:
type: array
items:
type: string
description: Filter by player ids. Player ids can be determined using the getPlayers function.
responses:
"200":
description: OK
tool参数
计算加法
tools=[{ # 用 JSON 描述函数。可以定义多个。由大模型决定调用谁。也可能都不调用
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "sum",
"description": "加法器,计算一组数的和",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"numbers": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "number"
}
}
}
}
}
}],
获取位置和查找位置,多fuction
tools=[{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_location_coordinate",
"description": "根据POI名称,获得POI的经纬度坐标",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "POI名称,必须是中文",
},
"city": {
"type": "string",
"description": "POI所在的城市名,必须是中文",
}
},
"required": ["location", "city"],
}
}
},
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "search_nearby_pois",
"description": "搜索给定坐标附近的poi",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"longitude": {
"type": "string",
"description": "中心点的经度",
},
"latitude": {
"type": "string",
"description": "中心点的纬度",
},
"keyword": {
"type": "string",
"description": "目标poi的关键字",
}
},
"required": ["longitude", "latitude", "keyword"],
}
}
}],
根据格式,找到重要变量,中文描述
配置函数功能
import requests
amap_key = "6d672e6194caa3b639fccf2caf06c342"
def get_location_coordinate(location, city="北京"):
url = f"https://restapi.amap.com/v5/place/text?key={amap_key}&keywords={location}®ion={city}"
print(url)
r = requests.get(url)
result = r.json()
if "pois" in result and result["pois"]:
return result["pois"][0]
return None
def search_nearby_pois(longitude, latitude, keyword):
url = f"https://restapi.amap.com/v5/place/around?key={amap_key}&keywords={keyword}&location={longitude},{latitude}"
print(url)
r = requests.get(url)
result = r.json()
ans = ""
if "pois" in result and result["pois"]:
for i in range(min(3, len(result["pois"]))):
name = result["pois"][i]["name"]
address = result["pois"][i]["address"]
distance = result["pois"][i]["distance"]
ans += f"{name}\n{address}\n距离:{distance}米\n\n"
return ans
其中涉及了key,也可以单纯用python工具,学会判断json中的值
nl2sql
tool代码
tools=[{ # 摘自 OpenAI 官方示例 https://github.com/openai/openai-cookbook/blob/main/examples/How_to_call_functions_with_chat_models.ipynb
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "ask_database",
"description": "Use this function to answer user questions about business. \
Output should be a fully formed SQL query.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"query": {
"type": "string",
"description": f"""
SQL query extracting info to answer the user's question.
SQL should be written using this database schema:
{database_schema_string}
The query should be returned in plain text, not in JSON.
The query should only contain grammars supported by SQLite.
""",
}
},
"required": ["query"],
}
}
}],
database_schema_string = """
CREATE TABLE orders (
id INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL, -- 主键,不允许为空
customer_id INT NOT NULL, -- 客户ID,不允许为空
product_id STR NOT NULL, -- 产品ID,不允许为空
price DECIMAL(10,2) NOT NULL, -- 价格,不允许为空
status INT NOT NULL, -- 订单状态,整数类型,不允许为空。0代表待支付,1代表已支付,2代表已退款
create_time TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, -- 创建时间,默认为当前时间
pay_time TIMESTAMP -- 支付时间,可以为空
);
"""
函数
def ask_database(query):
cursor.execute(query)
records = cursor.fetchall()
return records
prompt = "上个月的销售额"
# prompt = "统计每月每件商品的销售额"
# prompt = "哪个用户消费最高?消费多少?"
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "基于 order 表回答用户问题"},
{"role": "user", "content": prompt}
]
response = get_sql_completion(messages)
if response.content is None:
response.content = ""
messages.append(response)
print("====Function Calling====")
print(response)
if response.tool_calls is not None:
tool_call = response.tool_calls[0]
if tool_call.function.name == "ask_database":
arguments = tool_call.function.arguments
args = json.loads(arguments)
print("====SQL====")
print(args["query"])
result = ask_database(args["query"])
print("====DB Records====")
print(result)
messages.append({
"tool_call_id": tool_call.id,
"role": "tool",
"name": "ask_database",
"content": str(result)
})
response = get_sql_completion(messages)
print("====最终回复====")
print(response.content)
流式输出
stream参数=true 与tool参数同级
ChatGPT 流式输出是指 ChatGPT 在处理输入时,可以逐步生成回复,而不是一次性返回整个回复。这种输出方式对于处理长输入或复杂问题特别有用,因为它可以让我们更快地得到初步的回复,而不是等待整个回复生成完成。
流式输出的一个主要优点是它可以提高用户体验,让用户感觉系统响应更快。此外,对于一些应用场景,如实时对话或交互式应用程序,流式输出可以提供更自然的交互方式。
总的来说,ChatGPT 流式输出是一个有用的功能,可以让用户更快地得到初步回复,提高用户体验,适用于实时对话和交互式应用程序。
如果进行流式输出,必须对token进行拼接,拼接完毕才能去做后面的事情
代码
# 需要把 stream 里的 token 拼起来,才能得到完整的 call
for msg in response:
delta = msg.choices[0].delta
if delta.tool_calls:
if not function_name:
function_name = delta.tool_calls[0].function.name
args_delta = delta.tool_calls[0].function.arguments
print(args_delta)
args = args + args_delta
elif delta.content:
text_delta = delta.content
print(text_delta)
text = text + text_delta
ChatGLM3-6B
官方文档:https://github.com/THUDM/ChatGLM3/blob/main/tool_using/README.md
- 最著名的国产开源大模型,生态最好
- 早就使用 `tools` 而不是 `function` 来做参数,其它和 OpenAI 1106 版之前完全一样
NLP算法工程师视角: