特殊类设计
- 1.请设计一个类,不能被拷贝
- 2.请设计一个类,只能在堆上创建对象
- 3.请设计一个类,只能在栈上创建对象
- 4.请设计一个类,不能被继承
- 5.请设计一个类,只能创建一个对象(单例模式)
1.请设计一个类,不能被拷贝
拷贝只会放生在两个场景中:拷贝构造函数以及赋值运算符重载,因此想要让一个类禁止拷贝,只需让该类不能调用拷贝构造函数以及赋值运算符重载即可。
- C++98
将拷贝构造函数与赋值运算符重载只声明不定义,并且将其访问权限设置为私有即可。
class CopyBan { // ... private: CopyBan(const CopyBan&); CopyBan& operator=(const CopyBan&); //... };为什么只声明不实现呢?
因为自己不声明,库就会自动生成。因此只要自己写库就不会默认生成。
为什么声明私有呢?
如果声明为公有类外面可以实现别人就可以调用。
- C++11
C++11扩展delete的用法,delete除了释放new申请的资源外,如果在默认成员函数后跟上=delete,表示让编译器删除掉该默认成员函数。
class CopyBan { // ... CopyBan(const CopyBan&)=delete; CopyBan& operator=(const CopyBan&)=delete; //... };2.请设计一个类,只能在堆上创建对象
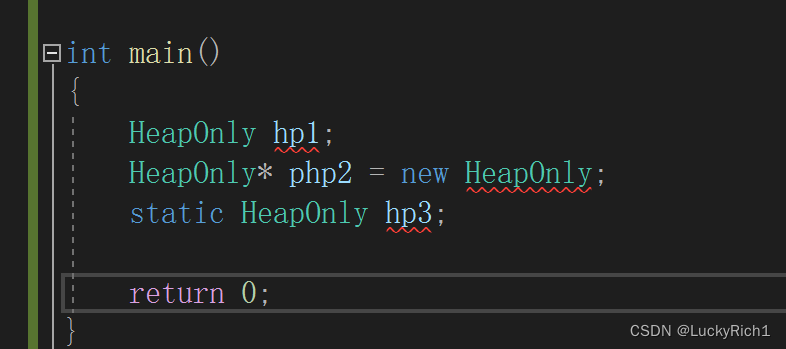
1.首先我们必须要把构造函数私有
如果不把构造私有分分钟钟就创建出三个对象,并且这三个对象在不同的位置栈、堆、静态区。
class HeapOnly { }; int main() { HeapOnly hp1; HeapOnly* php2 = new HeapOnly; static HeapOnly hp3; return 0; }因此把构造私有
class HeapOnly { private: HeapOnly() {} }; int main() { HeapOnly hp1; HeapOnly* php2 = new HeapOnly; static HeapOnly hp3; return 0; }这样类外面就调不了构造函数。外面就不随便创建对象!
但是我还是需要创建需要的对象,因此类内部写一个创建对象的成员函数
class HeapOnly { public: HeapOnly* CreateObj() { return new HeapOnly; } private: HeapOnly() {} };但是现在问题就来了,外面根本不能创建出对象,也就是说根本调不动CreteObj。
那怎么办呢?
2.提供一个静态的成员函数,在该静态成员函数中完成堆对象的创建
静态成员函数没有this指针,可以不用对象去调用,使用类域::类的成员函数调用
class HeapOnly { public: static HeapOnly* CreateObj() { return new HeapOnly; } private: HeapOnly() {} }; int main() { //HeapOnly hp1; //HeapOnly* php2 = new HeapOnly; //static HeapOnly hp3; HeapOnly* php4=HeapOnly::CreateObj(); return 0; }现在这个写法有没有什么地方没有考虑到?
就是不只在堆上,还可以在别的地方创建出对象,假如是栈。
int main() { HeapOnly* php4=HeapOnly::CreateObj(); //hp5在栈上! HeapOnly hp5(*php4);//拷贝构造 return 0; }3.防拷贝
class HeapOnly { public: static HeapOnly* CreateObj() { return new HeapOnly; } private: HeapOnly() {} HeapOnly(const HeapOnly&) = delete; //这里赋值不用delete的,自己不写编译器默认生成的是浅拷贝,对象还是在堆上 };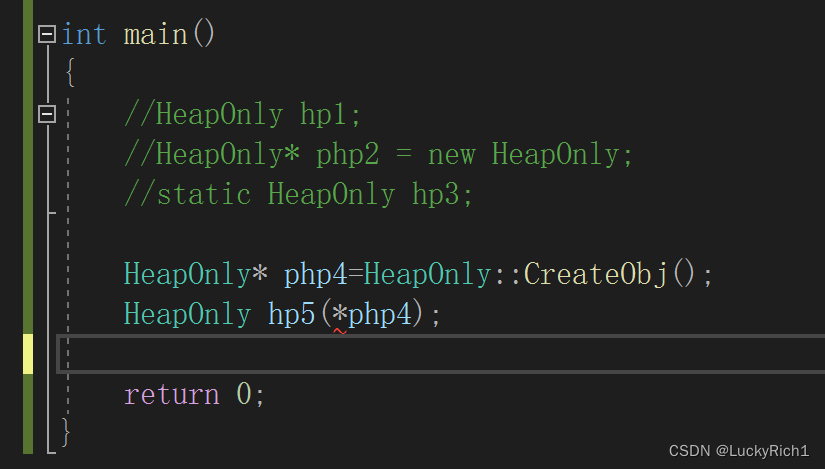
这是一种完整方法,只能在堆上创建对象!
还有一种方法析构函数私有+拷贝构造delete!
class HeapOnly { public: HeapOnly() {} private: ~HeapOnly() {} HeapOnly(const HeapOnly&) = delete; }; int main() { HeapOnly hp1; return 0; }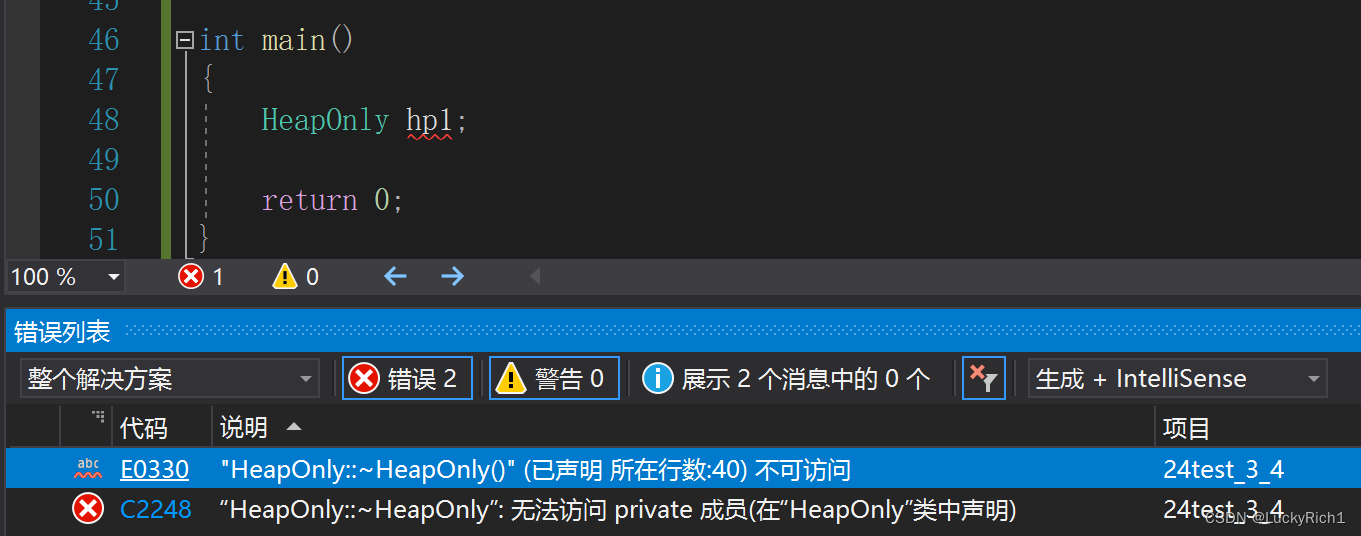
原因在于出了作用域会调用析构函数,这里不让调用编译就报错了。
这种写法确实只可以在堆上申请对象!但是有没有什么问题?
int main() { //HeapOnly hp1; HeapOnly* php2 = new HeapOnly; return 0; }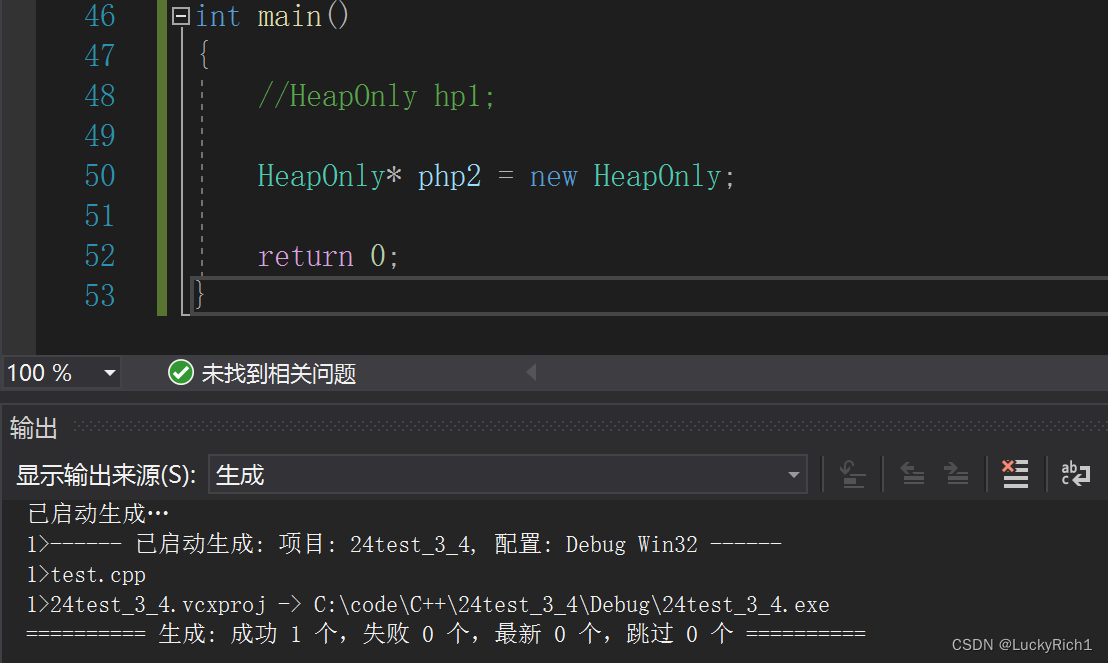
最显然就是没有办法delete释放资源了,有没有什么办法解决一下?
在类内部写一个Destory去释放资源。
class HeapOnly { public: HeapOnly() {} void Destory() { delete this; //或者调用显示调用析构1:对象.析构 2:this->析构 //this->~HeapOnly(); } private: ~HeapOnly() {} HeapOnly(const HeapOnly&) = delete; }; int main() { HeapOnly* php2 = new HeapOnly; php2->Destory(); return 0; }3.请设计一个类,只能在栈上创建对象
方法1:同上将构造函数私有化,然后设计静态方法创建对象返回
class StackOnly { public: static StackOnly CreateObj() { return StackOnly(); } private: StackOnly() {} }; int main() { StackOnly so1=StackOnly::CreateObj(); return 0; }还有一种方法说的禁掉new和delete。
因为new在底层调用void* operator new(size_t size),只需要将该函数屏蔽掉即可。
注意:也要防止定位new
class StackOnly { public: static StackOnly CreateObj() { return StackOnly(); } void* operator new(size_t size) = delete; void* operator delete(size_t size) = delete; //private: StackOnly() {} }; int main() { StackOnly so1=StackOnly::CreateObj(); StackOnly* pso = new StackOnly; //静态封不掉 static StackOnly so2; return 0; }这种方法是有问题的,如果只禁用operator new、operator delete,只是不想在堆上创建对象,但是可以在除了堆上的其他地方创建对象,全局、局部、静态都可以!
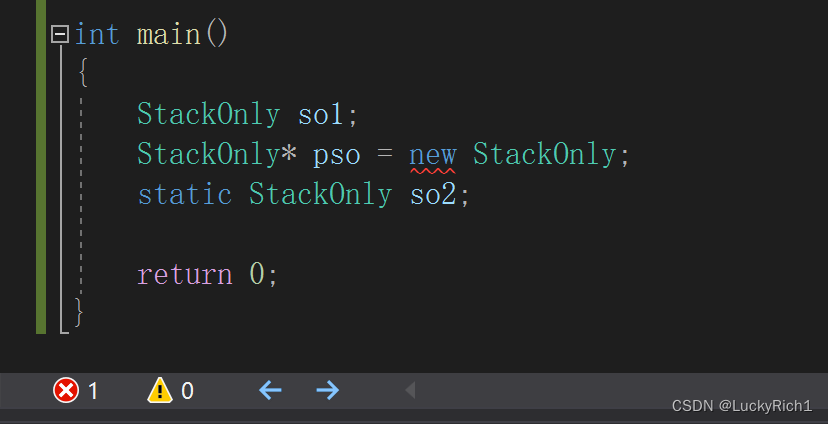
如果加上也可以,但是还是要把构造给封掉,不然静态还是可以的。
方法1的代码还有没有其他问题?
有的,方法1并没有把路封死!
class StackOnly { public: static StackOnly CreateObj() { return StackOnly(); } private: StackOnly() {} }; int main() { StackOnly so1=StackOnly::CreateObj(); static StackOnly so2 = StackOnly::CreateObj(); return 0; }静态对象还可以实现
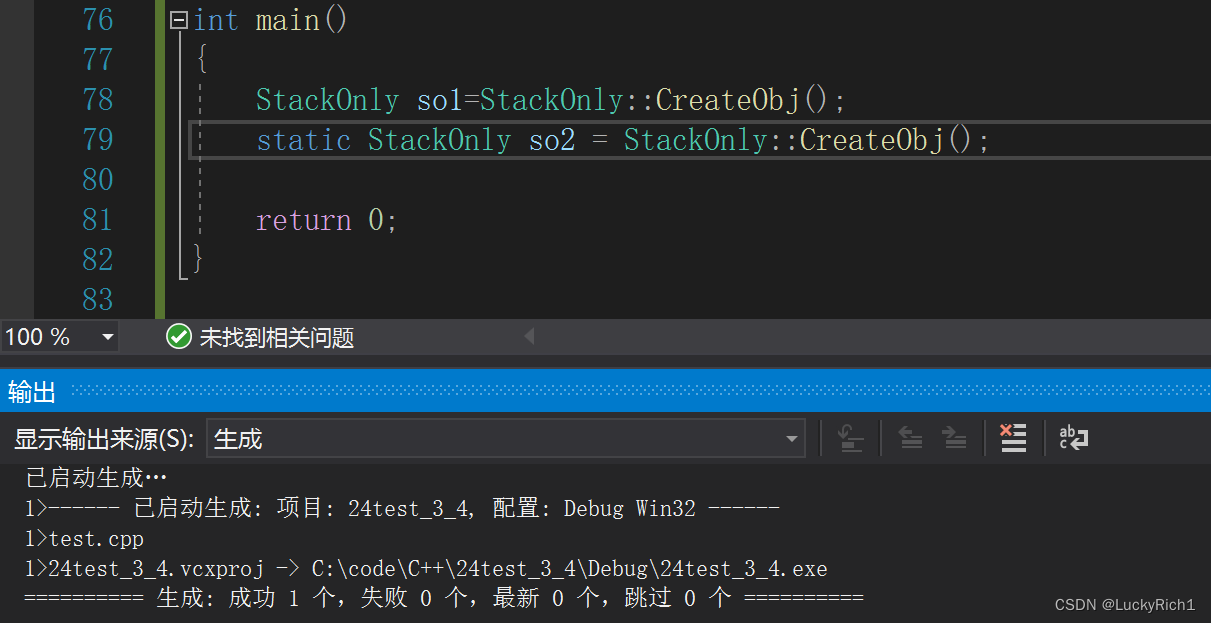
那把拷贝构造封掉试一试
class StackOnly { public: static StackOnly CreateObj() { return StackOnly(); } StackOnly(const StackOnly&) = delete; private: StackOnly() {} };但是这里又不行了
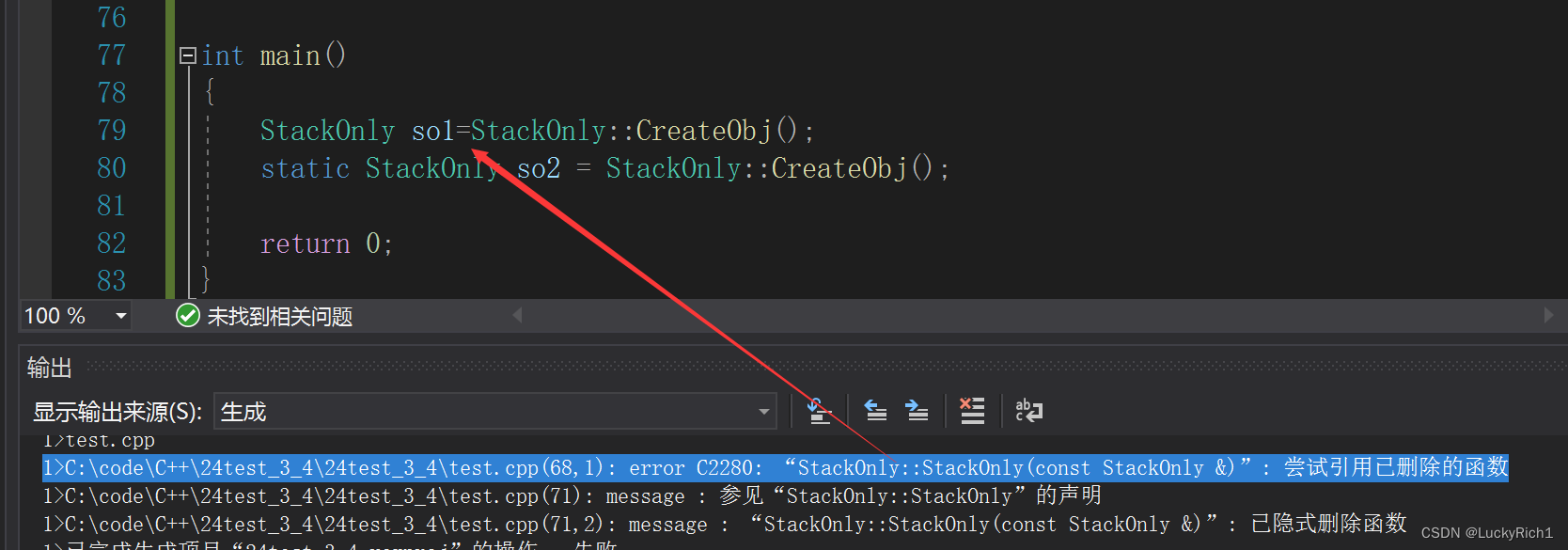
这里拷贝构造不行了,那我提供一个移动构造
class StackOnly { public: static StackOnly CreateObj() { return StackOnly(); } StackOnly(StackOnly&&) {} StackOnly(const StackOnly&) = delete; private: StackOnly() {} };但这里又行了
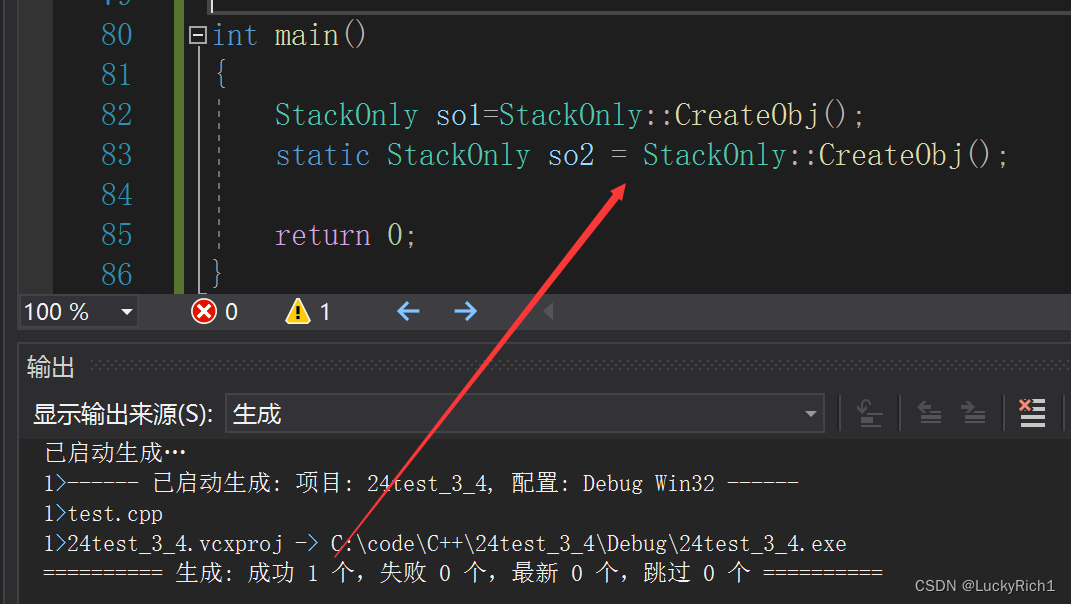
这里想说的是这个类封不死!静态的确实没有很好的办法解决。
如果真的把这里封死就一种办法,把拷贝构造封死,不让用的人这样使用。
class StackOnly { public: static StackOnly CreateObj() { return StackOnly(); } //StackOnly(StackOnly&&) //{} void Print() const { cout } }; int main() { //不用这样使用 //StackOnly so1=StackOnly::CreateObj(); //static StackOnly so2 = StackOnly::CreateObj(); //而是这样用 //1. StackOnly::CreateObj().Print(); //2. const StackOnly& so1= StackOnly::CreateObj(); so1.Print(); return 0; } public: static NonInherit GetInstance() { return NonInherit(); } private: NonInherit() {} }; // .... }; public: private: InfoSingleton() {} map //InfoSingleton s1; //InfoSingleton s2; //InfoSingleton s3; return 0; } public: static InfoSingleton& GetInstance() { } private: InfoSingleton() {} map public: static InfoSingleton& GetInstance() { } private: InfoSingleton() {} map public: static InfoSingleton& GetInstance() { //直接返回就行 return _sins; } private: InfoSingleton() {} map InfoSingleton::GetInstance(); return 0; } public: static InfoSingleton& GetInstance() { return _sins; } void insert(string name, int salary) { _info[name] = salary; } void Print() { for (auto& kv : _info) { cout } map //1. InfoSingleton::GetInstance().insert("张三",10000); //2. InfoSingleton& infos1 = InfoSingleton::GetInstance(); infos1.insert("李四", 15000); infos1.insert("王五", 30000); infos1.Print(); return 0; } //1. InfoSingleton::GetInstance().insert("张三",10000); //2. InfoSingleton& infos1 = InfoSingleton::GetInstance(); infos1.insert("李四", 15000); infos1.insert("王五", 30000); infos1.Print(); //拷贝构造 InfoSingleton copy = InfoSingleton::GetInstance(); copy.insert("赵六", 20000); copy.Print(); infos1.Print(); return 0; } public: static InfoSingleton& GetInstance() { return _sins; } void insert(string name, int salary) { _info[name] = salary; } void Print() { for (auto& kv : _info) { cout } InfoSingleton(const InfoSingleton& info) = delete; InfoSingleton& operator=(const InfoSingleton& info) = delete; map //1. InfoSingleton::GetInstance().insert("张三",10000); //2. InfoSingleton& infos1 = InfoSingleton::GetInstance(); infos1.insert("李四", 15000); infos1.insert("王五", 30000); infos1.Print(); //拷贝构造 //InfoSingleton copy = InfoSingleton::GetInstance(); //copy.insert("赵六", 20000); //copy.Print(); infos1.Print(); return 0; } public: //这里可以也可以返回指针 static InfoSingleton& GetInstance() { //第一次获取单例对象的时候创建对象 if (_psins == nullptr) { _psins = new InfoSingleton; } return *_psins; } void insert(string name, int salary) { _info[name] = salary; } void Print() { for (auto& kv : _info) { cout } InfoSingleton(const InfoSingleton& info) = delete; InfoSingleton& operator=(const InfoSingleton& info) = delete; map public: //这里可以也可以返回指针 static InfoSingleton& GetInstance() { _smtx.lock(); if (_psins == nullptr) { _psins = new InfoSingleton; } _smtx.unlock(); return *_psins; } void insert(string name, int salary) { _info[name] = salary; } void Print() { for (auto& kv : _info) { cout } InfoSingleton(const InfoSingleton& info) = delete; InfoSingleton& operator=(const InfoSingleton& info) = delete; map //第一次if,对象new出来之后,避免每次都加锁的检查,提高性能 if (_psins == nullptr) { _smtx.lock(); //第二次if,保证线程安全且只能new一次 if (_psins == nullptr) { _psins = new InfoSingleton; } _smtx.unlock(); } return *_psins; } if (_psins == nullptr) { _smtx.lock(); try { if (_psins == nullptr) { _psins = new InfoSingleton; } } catch (...) { _smtx.unlock(); throw; } } return *_psins; } public: LockGuard(Lock& mtx) :_mtx(mtx)//锁不能拷贝构造,1.传锁的地址过来 2.私有成员给个引用 { _mtx.lock(); } ~LockGuard() { _mtx.unlock(); } private: Lock& _mtx;//引用的成员变量,必须在初始化列表初始化 }; class InfoSingleton { public: //这里可以也可以返回指针 static InfoSingleton& GetInstance() { if (_psins == nullptr) { LockGuard _psins = new InfoSingleton; } //_smtx.unlock(); } return *_psins; } //。。。。 }; if (_psins == nullptr) { std::lock_guard _psins = new InfoSingleton; } } return *_psins; } //保存数据到文件 //... std::lock_guard delete _psins; _psins = nullptr; } } public: static InfoSingleton& GetInstance() { if (_psins == nullptr) { std::lock_guard _psins = new InfoSingleton; } } return *_psins; } static void DelInstance() { //保存数据到文件 //... std::lock_guard delete _psins; _psins = nullptr; } } class GC//内部类是外部类有元 { public: ~GC() { if (_psins) { DelInstance();//所以这里可以直接调 } } }; //。。。 private: static InfoSingleton* _psins; static mutex _smtx; static GC _gc; }; InfoSingleton* InfoSingleton::_psins=nullptr; mutex InfoSingleton::_smtx; InfoSingleton::GC InfoSingleton::_gc;//定义一个GC类的对象,main函数结束之后会自动调用GC的析构函数 public: //静态函数中写个该类静态对象 static InfoSingleton& GetInstance() { static InfoSingleton sinst; return sinst; } //。。。 private: InfoSingleton() { cout
- C++11
- C++98