🔥个人主页: Forcible Bug Maker
🔥专栏: STL || C++
目录
- 前言
- 🔥字符串操作(String operations)
- ==c_str==
- ==data==
- ==get_allocator==
- ==copy==
- ==find==
- ==rfind==
- ==find_first_of==
- ==find_last_of==
- ==find_first_not_of==
- ==find_last_not_of==
- ==substr==
- ==compare==
- 🔥常量成员(Member constants)
- ==npos==
- 结语
前言
本篇博客主要内容:STL库中string的字符串操作(String operations)和常量成员(Member constants)。
来到string类的使用第四篇,继续我们的内容,本篇博客将着重介绍如何使用string类提供的接口函数去查找和获取字符串的内容;同时还会讲一个定义在string类中的常量成员(npos)。
本篇也将是string类使用的收尾篇。
🔥字符串操作(String operations)
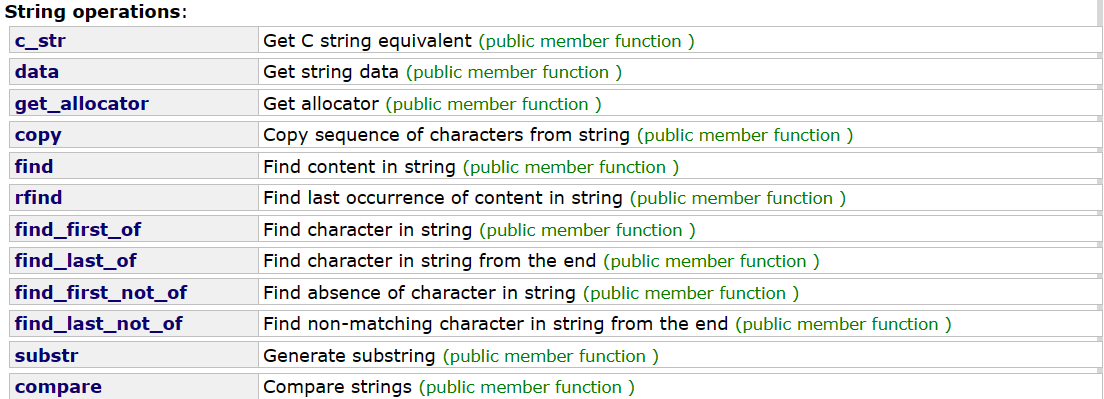
这些接口函数提供的是一些查找和获取string串内容的功能。
c_str

const char* c_str() const;
返回一个指向字符串数组(以'\0'结尾)的指针,代表当前string串的内容。
同时返回指针指向的字符串中的内容也是不可修改的。
使用案例:
// strings and c-strings #include #include #include using namespace std; int main() { std::string str("Hello World!"); char* cstr = new char[str.length() + 1]; strcpy(cstr, str.c_str()); printf("%s\n", str.c_str()); printf("%s\n", cstr); return 0; }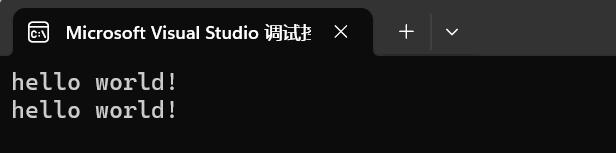
简单来说c_str就是获取一个字符串指针,指向的就是string对量串中的内容。
data

const char* data() const;
返回一个指向数组的指针。(该数组与string串构成字符相同,不保证字符串数组以'\0'结尾。c_str能保证)
使用案例:
// string::data #include #include #include using namespace std; int main() { int length; std::string str = "Test string"; const char* cstr = "Test string"; if (str.length() == strlen(cstr)) { cout char buffer[20]; string str("Test string..."); size_t length = str.copy(buffer, 6, 5); buffer[length] = '\0'; cout string str("There are two needles in this haystack with needles."); string str2("needle"); // different member versions of find in the same order as above: size_t found = str.find(str2); if (found != string::npos) cout