1. unordered系列关联式容器
STL提供了底层为红黑树结构的一系列关联式容
这里介绍 unordered_set 和 unordered_map
a. unordered_map
- unordered_map 是存储键值对的关联式容器,其允许通过 key 快速的索引到与
其对应的 value
- unordered_map 容器通过 key 访问单个元素要比 map 快,但它通常在遍历元素子集的范围迭
代方面效率较低
b. unordered_set
- unordered_set 允许通过 key 快速的索引是否存在
- 重复数据可以去重
- 删除,查找,插入,效率都很快
2. unordered_map 的接口说明
a. unordered_map 的容量
函数声明
1. bool empty() const
2. size_t size() const
1. 检测unordered_map是否为空
2. 获取unordered_map的有效元素个数
b. unordered_map 的迭代器
函数声明
1. iterator begin()
2. iterator end()
3. iterator cbegin() const
4. iterator cend() const
功能介绍
1. 返回 unordered_map 第一个元素的迭代器
2. 返回 unordered_map 最后一个元素下一个位置的迭代器
3. 返回 unordered_map 第一个元素的const迭代器
4. 返回 unordered_map 最后一个元素下一个位置的const迭代器
c. unordered_map 的元素访问
函数声明
1. K& operator[]
功能介绍
1. 返回与 key 对应的 value ,允许被修改
d. unordered_map 的查询
函数声明
1. iterator find(const K& key)
2. size_t count(const K& key)
功能介绍
1. 返回key在哈希桶中的位置
2. 返回哈希桶中关键码为key的键值对的个数
注意:
unordered_map 中 key 是不能重复的,因此 count函数的返回值最大为 1
e. unordered_map 的桶操作
函数声明
1. size_t bucket_count() const
2. size_t bucket_size(size_t n) const
3. size_t bucket(const K& key)
功能介绍
1. 返回哈希桶中桶的总个数
2. 返回n号桶中有效元素的总个数
3. 返回元素key所在的桶号
注意:
unordered_set 用法差不多,就不介绍了
3. 哈希概念
通过位置关系找到对应的 key
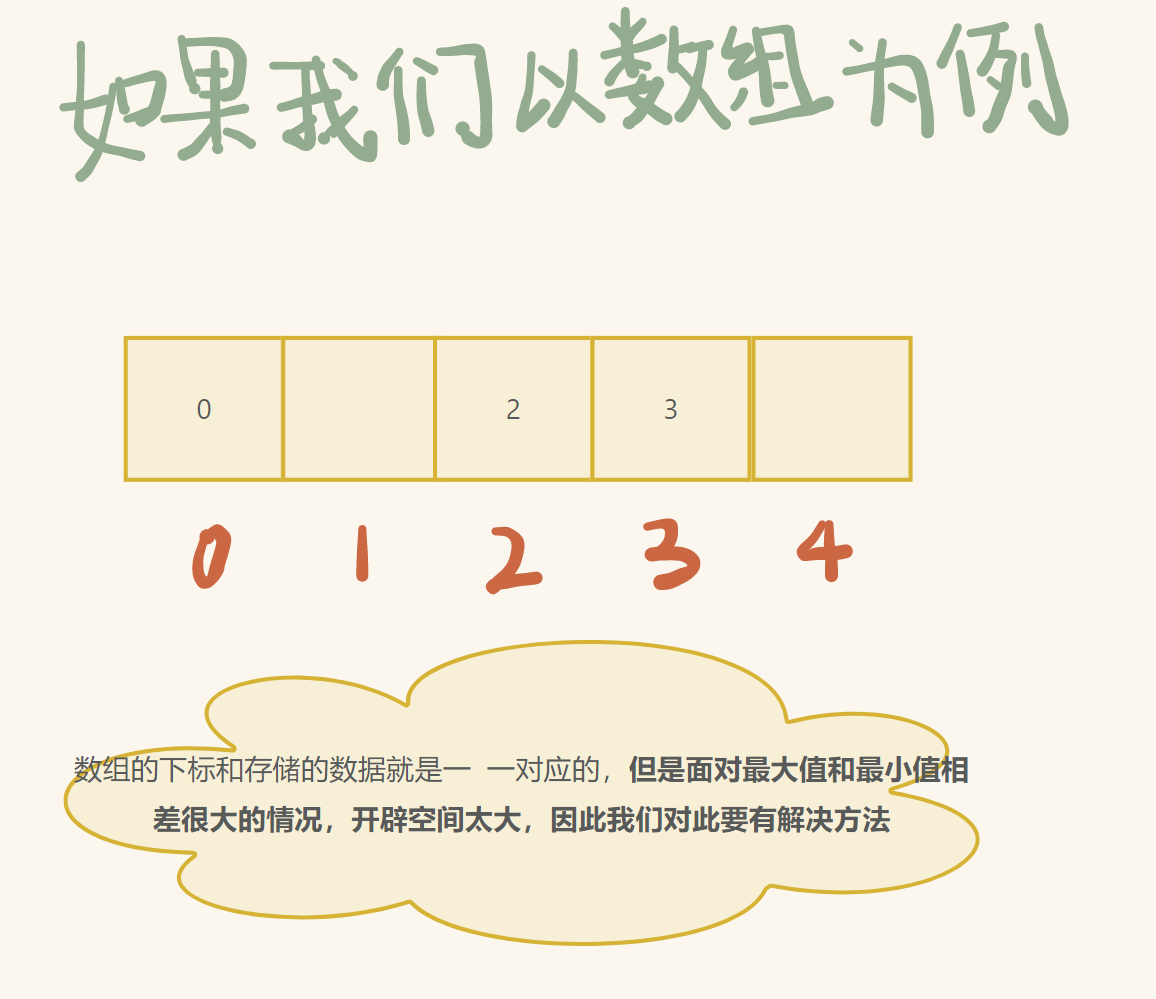
a. 哈希冲突解决
先说上述问题的解决:
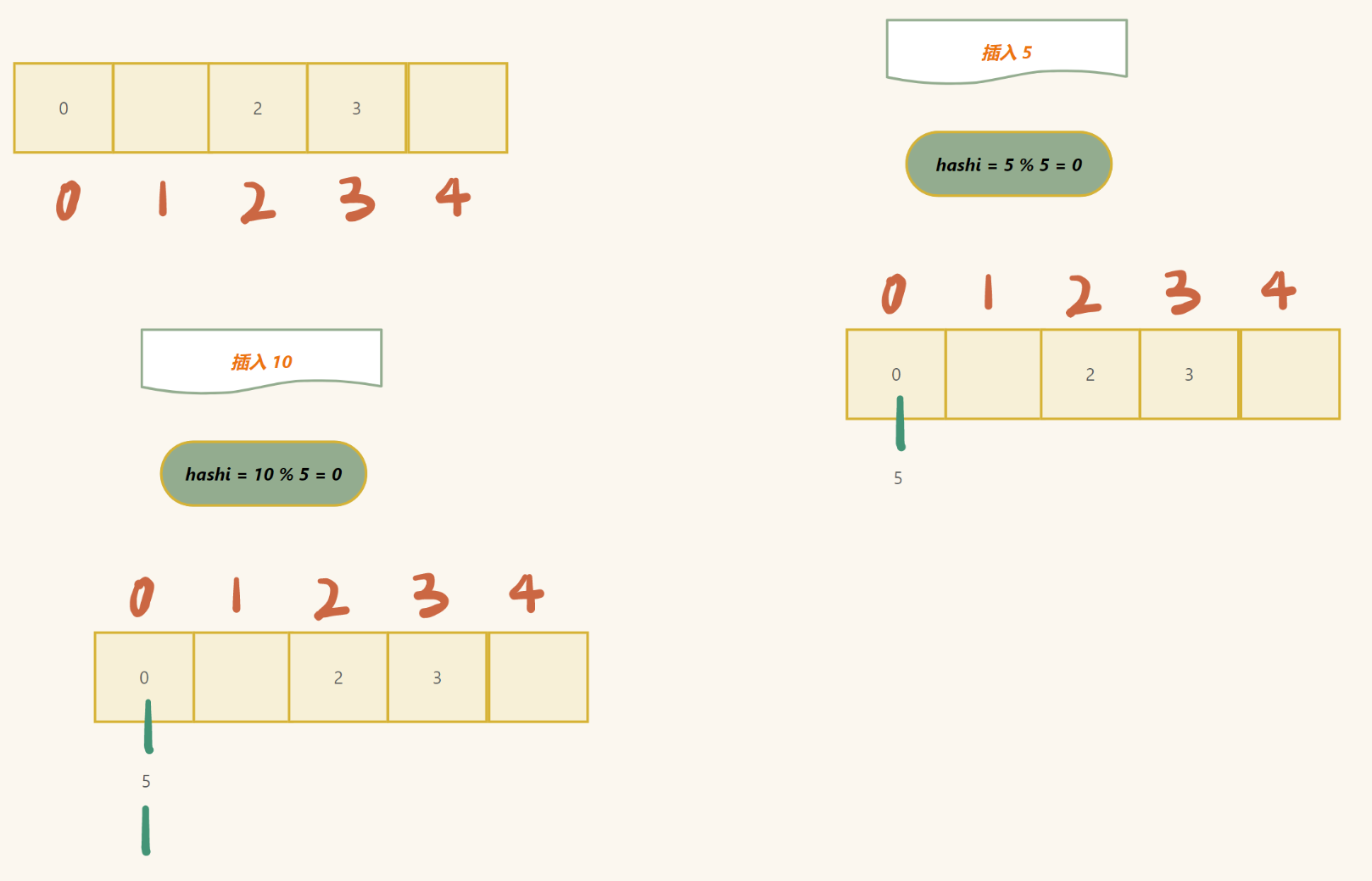
hashi (数组下标) = key % n (若 key 不为整数, 另做处理)
但是在插入的过程中,我们容易遇到以下问题:
- hashi 已经有数值存入 (这种问题又叫 哈希冲突 )
第一种方法:(闭散列)
如果是这种情况,直接往后找,直到遇到空位置 (数组里面存入什么值都很难表示这个位置的状态,所以我们自己可以加入)
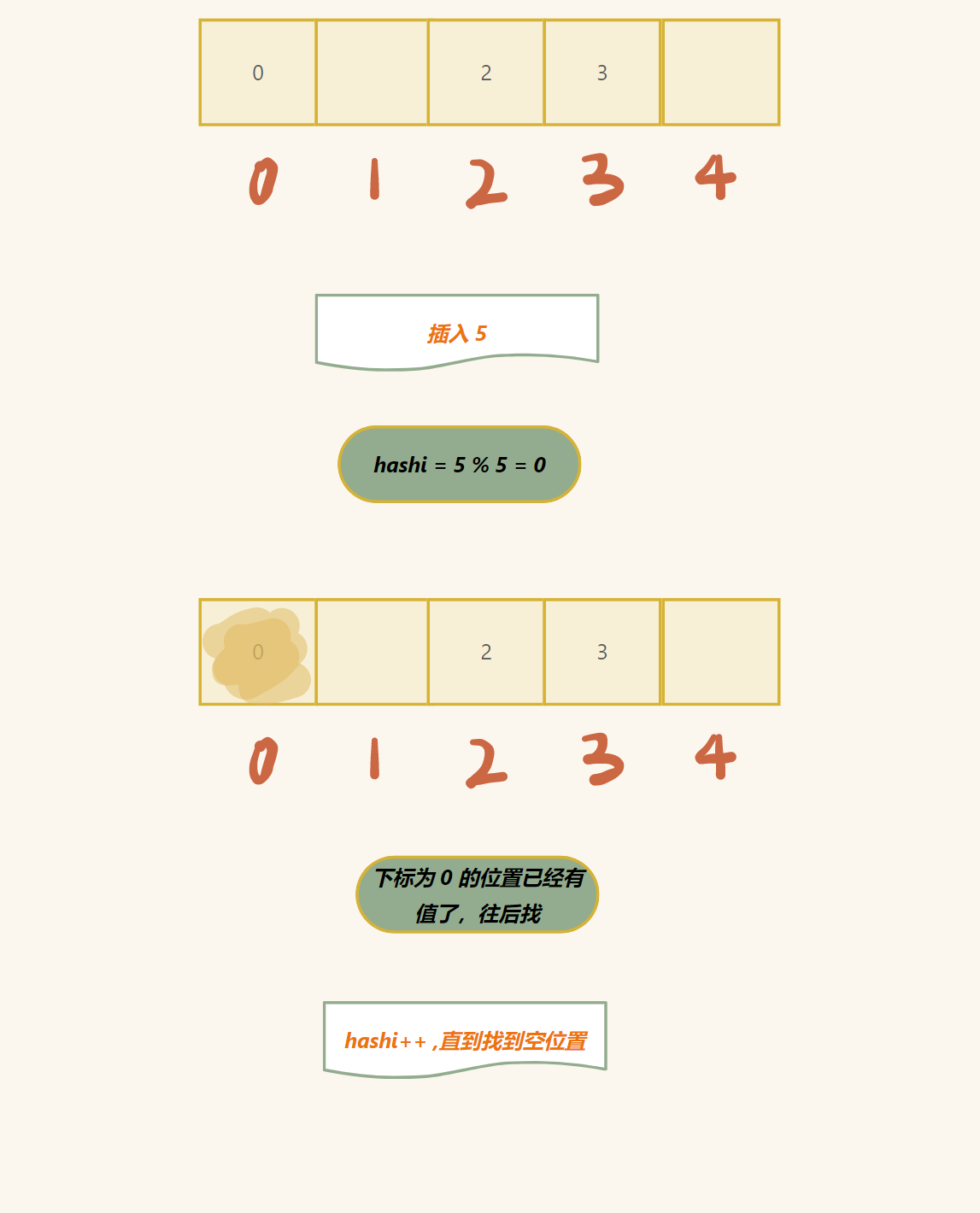
2. 所有的位置都有没有位置了
这种问题一定要涉及到空间的开辟 (但是这里我们需要谈论的是什么时候扩空间比较好)
注意:
这种分情况,后面实现再讲
另外一种方法解决(开散列):
开散列法又叫链地址法(开链法),首先对关键码集合用散列函数计算散列地址,具有相同地
址的关键码归于同一子集合,每一个子集合称为一个桶,各个桶中的元素通过一个单链表链
接起来,各链表的头结点存储在哈希表中
4. 闭散列实现
代码
enum State
{
Empty,
Exist,
Delete
};
template
struct HashTable
{
pair _table;
State _state = Empty;
};
template
class Hsah
{
public:
bool insert(const pair& kv)
{
if (_t.size() == 0 || n * 10 / _t.size() >= 7)
{
Hsah x;
size_t size = _t.size() == 0 ? 10 : _t.size() * 2;
x._t.resize(size);
for (auto i : _t)
{
if (i._state == Exist)
{
x.insert(i._table);
}
}
_t.swap(x._t);
}
size_t hashi = kv.first % _t.size();
int index = hashi;
size_t i = 1;
while (_t[index]._state != Empty)
{
index = hashi + i;
index %= _t.size();
i++;
}
_t[index]._table = kv;
_t[index]._state = Exist;
n++;
return true;
}
HashTable* find(const K& key)
{
if (_t.size() == 0)
{
return nullptr;
}
size_t hashi = key % _t.size();
int index = hashi;
size_t i = 1;
while (_t[index]._state != Empty)
{
if (_t[index]._table.first == key)
{
if (_t[index]._state == Delete)
{
return nullptr;
}
return &_t[index];
}
index = hashi + i;
index %= _t.size();
i++;
if (index == hashi)
{
break;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
HashTable* t = find(key);
if (t == nullptr || t->_state == Delete)
{
return false;
}
t->_state = Delete;
}
private:
size_t n = 0;
vector _t;
};
5. 开散列实现
代码
template
struct HashNode
{
HashNode(const pair& kv)
:_kv(kv)
,next(nullptr)
{}
HashNode* next;
pair _kv;
};
template
class HashBucket
{
public:
typedef HashNode Node;
void insert(const pair& kv)
{
if (n == _hash.size())
{
size_t newsize = _hash.size() == 0 ? 10 : _hash.size() * 2;
vector newnode(newsize, nullptr);
for (auto cur : _hash)
{
while (cur)
{
int hashi = cur->_kv.first % newsize;
Node* prev = newnode[hashi];
newnode[hashi] = cur;
cur->next = prev;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
_hash.swap(newnode);
}
int hashi = kv.first % _hash.size();
Node* cur = new Node(kv);
Node* _next = _hash[hashi];
_hash[hashi] = cur;
cur->next = _next;
n++;
}
bool find(const K& key)
{
if (_hash.size() == 0)
{
return false;
}
int hashi = key % _hash.size();
Node* cur = _hash[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first = key)
{
return true;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return false;
}
Node* erase(const K& key)
{
int hashi = key % _hash.size();
Node* prev = nullptr;
Node* cur = _hash[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first = key)
{
if (prev == nullptr)
{
_hash[hashi] = cur->next;
}
else
{
prev->next = cur->next;
}
delete cur;
break;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
return nullptr;
}
private:
size_t n = 0;
vector _hash;
};
//这里插入选择了头插
6. unordered_map , unordered_set 底层实现
代码
“test.h” :
#pragma once
template
struct Compare
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
template
struct Compare
{
size_t operator()(const string& k)
{
size_t x = 0;
for (auto i : k)
{
x += i;
x *= 31;
}
return x;
}
};
namespace unordered
{
template
struct HashNode
{
HashNode(const T& data)
:_data(data)
, next(nullptr)
{}
HashNode* next;
T _data;
};
template
class HashBucket;
template
struct HashIterator
{
typedef typename HashIterator Self;
typedef HashNode Node;
HashIterator(Node* hash,const HashBucket* x)
:_node(hash)
,p(x)
{}
Self& operator++()
{
if (_node->next)
{
_node = _node->next;
}
else
{
Key0f kf;
int hashi = compare()(kf(_node->_data)) % (p->_hash.size());
++hashi;
while (hashi _hash.size())
{
if (p->_hash[hashi])
{
_node = p->_hash[hashi];
break;
}
else
{
++hashi;
}
}
if (hashi == p->_hash.size())
{
_node = nullptr;
}
}
return *this;
}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& ptr)
{
return _node != ptr._node;
}
const HashBucket* p;
Node* _node;
};
template
class HashBucket
{
template
friend class HashIterator;
public:
typedef HashNode Node;
typedef typename HashBucket Self;
typedef typename HashIterator Iterator;
typedef typename HashIterator const_Iterator;
Iterator begin()
{
for (int i = 0; i _data)) % newsize;
Node* prev = newnode[hashi];
newnode[hashi] = cur;
cur->next = prev;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
_hash.swap(newnode);
}
int hashi = compare()(kf(data)) % _hash.size();
Node* cur = new Node(data);
Node* _next = _hash[hashi];
_hash[hashi] = cur;
cur->next = _next;
n++;
return make_pair(Iterator(cur,this), true);
}
Iterator find(const K& key)
{
Key0f kf;
if (_hash.size() == 0)
{
return Iterator(nullptr,this);
}
int hashi = compare()(key) % _hash.size();
Node* cur = _hash[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (kf(cur->_data) == key)
{
return Iterator(cur, this);
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return Iterator(nullptr, this);
}
T* erase(const K& key)
{
Key0f kf;
int hashi = compare()(key) % _hash.size();
Node* prev = nullptr;
Node* cur = _hash[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (kf(cur->_data) == key)
{
if (prev == nullptr)
{
_hash[hashi] = cur->next;
}
else
{
prev->next = cur->next;
}
delete cur;
break;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
return nullptr;
}
private:
size_t n = 0;
vector _hash;
};
}
"my_map.h" :
#pragma once
#include "test.h"
template
class map
{
struct MapOf
{
const K& operator()(const pair& _key)
{
return _key.first;
}
};
public:
typedef typename unordered::HashBucket::const_Iterator Iterator;
typedef typename unordered::HashBucket::const_Iterator const_Iterator;
pair insert(const pair& data)
{
return pair(const_Iterator(key.insert(data).first._node,&key), key.insert(data).second);
}
Iterator find(const K& data)
{
return key.find(data);
}
pair* erase(const K& data)
{
return key.erase(data);
}
const_Iterator begin() const
{
return key.begin();
}
const_Iterator end() const
{
return key.end();
}
V& operator[](const K& k)
{
pair ret = key.insert(make_pair(k,V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
private:
unordered::HashBucket key;
};
"my_set.h" :
#pragma once
#include "test.h"
template
class set
{
struct SetOf
{
const K& operator()(const K& _key)
{
return _key;
}
};
public:
typedef typename unordered::HashBucket::const_Iterator Iterator;
typedef typename unordered::HashBucket::const_Iterator const_Iterator;
pair insert(const K& data)
{
return pair(const_Iterator(key.insert(data).first._node,&key), key.insert(data).second);
}
Iterator find(const K& data)
{
return key.find(data);
}
const K* erase(const K& data)
{
return key.erase(data);
}
const_Iterator begin() const
{
return key.begin();
}
const_Iterator end() const
{
return key.end();
}
private:
unordered::HashBucket key;
};
仿函数实现分析
”test.h“ 中:

其中:

这个完成了偏特化,将 string 可以变成 整型数,方便计算下标 hashi
细节注意
”my_map.h“ 中 :

”my_set.h“ 中 :

确保 map 和 set 都可以使用,
如果类型是 map ,得到的就是 pair里面的 K 类型
如果类型是 set ,得到的就是 K 类型
迭代器问题分析
由于在operator++过程中,需要访问HashBucket的成员变量,所以需要友元
且在构造时需要HashBucket类,则需要前置声明
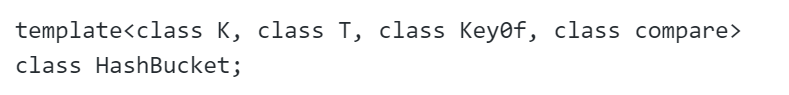
(前置声明)
迭代器注意:
pair insert(const pair& data)
{
return pair(const_Iterator(key.insert(data).first._node,&key), key.insert(data).second);
}
// return pair(key.insert(data)) 是错误的
key.insert(data)是 pair 类型,普通迭代器不能转换成 const迭代器