文章目录
- 📝再谈构造函数
- 🌠 构造函数体赋值
- 🌉初始化列表
- 🌉初始化列表效率
- 🌠隐式类型转换
- 🌉复制初始化
- 🌠单多参数构造函数
- 🌉explicit关键字
- 🚩总结
📝再谈构造函数
🌠 构造函数体赋值
在创建对象时,编译器通过调用构造函数,给对象中各个变量一个合适的初始值
class Date { public: Date(int year, int month, int day) { _year = year; _month = month; _day = day; } private: int _year; int _month; int _day; };虽然上面构造函数调用之后,对象中已经有了一个初始值,但是不能将其称为对对象中成员变量的初始化,构造函数体中的语句只能将其称为赋初值,这和我们之间常常说的给缺省值其实就是赋初值,而不能称作初始化。因为初始化只能初始化一次,而构造函数体内可以多次赋值。
🌉初始化列表
初始化列表:以一个冒号开始,接着是一个逗号分隔的数据成员列表,每个“成员变量”后面跟一个放在括号的初始化或表达式
class Date { public: Date(int year,int month,int day) :_year(year) ,_month(month) ,_day(day) { // } private: int _year; int _month; int _day; };为什么要有初始化列表来赋初值,不能直接给缺省值,或者传参吗?
class Date { public: Date(int year, int month, int day) { _year = year; _month = month; _day = day; _x = 1; } private: int _year; int _month; int _day; //必须在定义初始化 const int _x; };由于const必须在定义时就要进行初始化,而这个在构造函数中_x=1的行为是赋值行为,不是初始化,因此const 修饰_x无法再赋值。引用&也是如此,需要在定义的时候并且进行初始化,不能分开。
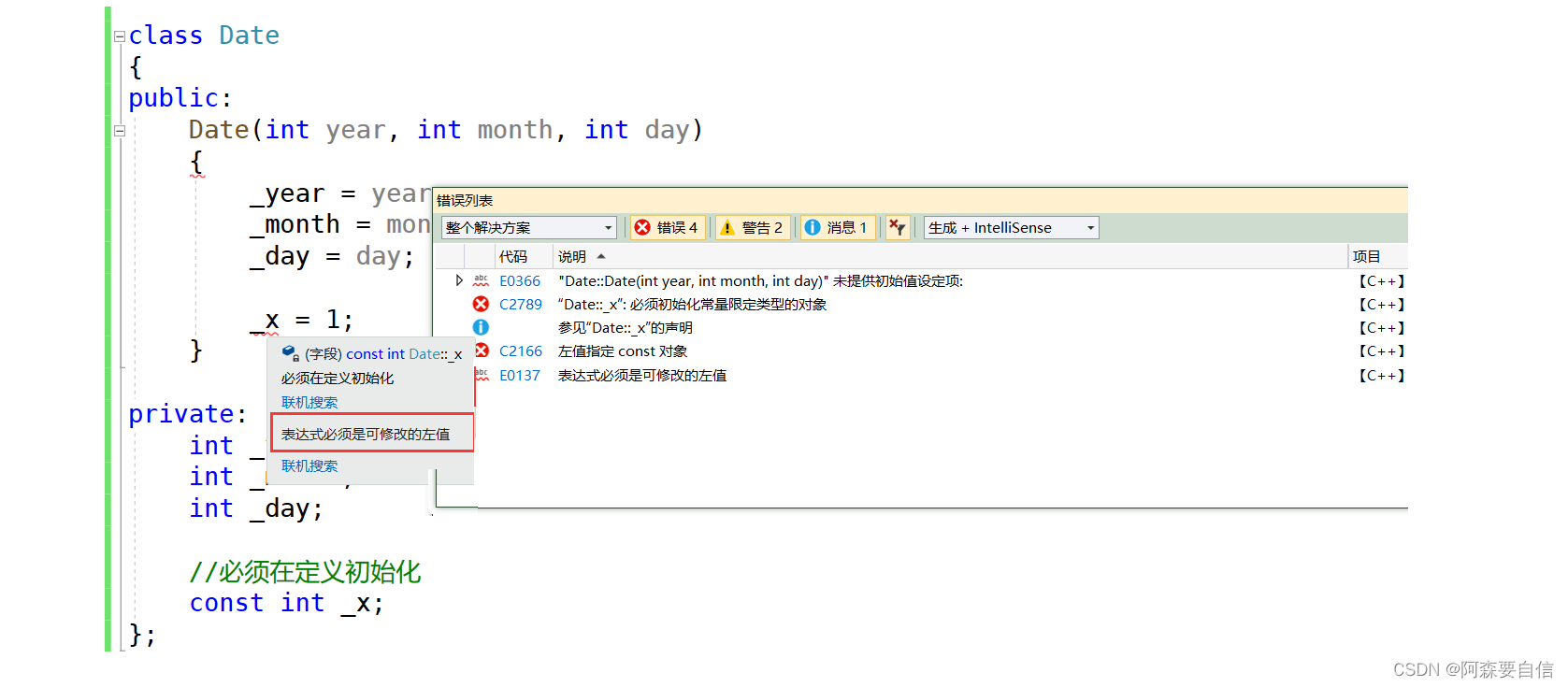
因此对于普通的内置类型,普通成员变量都可以在函数体或者在初始化列表进行初始化,
int _year; int _month; int _day;
因为在这里只是声明,没有定义,定义时实例化的时候完成的,而有些特殊的成员变量需要再定义的时候就初始化,而不是再通过赋值。
class Date { public: Date(int year, int month, int day, int& refDay) : ref(refDay) , _x(1) { _year = year; _month = month; _day = day; } void printDate() { std::cout int someDay = 22; Date date1(2024, 4, 22, someDay); date1.printDate(); return 0; } public: A(int a) :_a(a) {} private: int _a; }; class B { public: B(int a, int ref) :_aobj(a) , _ref(ref) , _n(10) {}; private: A _aobj; // 没有默认构造函数 int& _ref; //引用 const int _n;//const }; int main() { int x = 10; B bb(20, x); return 0; } public: Date(int year, int month, int day, int& refDay) : ref(refDay) , _x(1) { _year = year; _month = month; _day = day; } private: int _year; int _month; int _day; int& ref; const int _x; }; public: Stack(size_t capacity = 4) { _array = (DataType*)malloc(sizeof(DataType) * capacity); if (NULL == _array) { perror("malloc申请空间失败!!!"); return; } _capacity = capacity; _size = 0; } void Push(DataType data) { // CheckCapacity(); _array[_size] = data; _size++; } // 其他方法... ~Stack() { if (_array) { free(_array); _array = NULL; _capacity = 0; _size = 0; } } private: DataType* _array; int _capacity; int _size; }; class MyQueue { public: // 初始化列表,不管你写不写,每个成员变量都会先走一遍 // 自定义类型的成员会调用默认构造(没有默认构造就编译报错) // 内置类型有缺省值用缺省值,没有的话,不确定,要看编译器,有的编译器会处理,有的不会处理 // 先走初始化列表 + 再走函数体 // 实践中:尽可能使用初始化列表初始化,不方便再使用函数体初始化 MyQueue() :_size(1) , _ptr((int*)malloc(40)) { memset(_ptr, 0, 40); } private: // 声明 Stack _pushst; Stack _popst; // 缺省值 给初始化列表用的 int _size = 0; const int _x = 10; int* _ptr; }; int main() { MyQueue q; return 0; } public: A(int a) :_a1(a) ,_a2(_a1) {} void Print() { cout A aa(1); aa.Print(); } A. 输出1 1 B.程序崩溃 C.编译不通过 D.输出1 随机值 public: A(int a) :_a1(a) ,_a2(_a1) {} void Print() { cout A aa(1); aa.Print(); } //... A(); //默认构造函数 A(const A& d); //拷贝构造函数 A& operator=(const A& d); //赋值函数 }; class B { public: B(const A& a); //B的成员对象 private: A m_a; //成员对象 }; ... } m_a = a; ... } public: A(int a) :_a(a) { cout A aa1(1); //拷贝构造 A aa2 = aa1; A aa3 = 3; return 0; } public: A(int a) :_a(a) { cout cout A aa1(1); A aa3 = 3; return 0; } public: A(int a) :_a(a) { cout A& raa = 3; return 0; } public: void Push(const A& aa) { //... } //... }; int main() { Stack st; A a1(1); st.Push(a1); A a2(2); st.Push(a2); //可以直接写 st.Push(2); st.Push(4); return 0; } list} A aaa1(1, 2); A aaa2 = { 1, 2 }; const A& aaa3 = { 1, 2 }; public: // 1. 单参构造函数,没有使用explicit修饰,具有类型转换作用 // explicit修饰构造函数,禁止类型转换---explicit去掉之后,代码可以通过编译 explicit Date(int year) :_year(year) {} /* // 2. 虽然有多个参数,但是创建对象时后两个参数可以不传递,没有使用explicit修饰,具有类型转 换作用 // explicit修饰构造函数,禁止类型转换 explicit Date(int year, int month = 1, int day = 1) : _year(year) , _month(month) , _day(day) {} */ Date& operator=(const Date& d) { if (this != &d) { _year = d._year; _month = d._month; _day = d._day; } return *this; } private: int _year; int _month; int _day; }; void Test() { Date d1(2022); // 用一个整形变量给日期类型对象赋值 // 实际编译器背后会用2023构造一个无名对象,最后用无名对象给d1对象进行赋值 d1 = 2023; // 将1屏蔽掉,2放开时则编译失败,因为explicit修饰构造函数,禁止了单参构造函数类型转换的作 用 }