目錄

1、函數表現形式
分類

lambda表達式
- 參數類型可以全寫,也可以全不寫,但不能一部分寫,一部分不寫
- lambda 的省略策略:凡是可推導,都可以省略

方法引用

練習-判斷語法正确性

練習-寫出與方法引用等價的lambda表達式
實體類
Student 類有一個屬性 name
Pythonpublic class Student { private string name; public Student (String name){ this.name = name; } public Student(){ } public String getName(){ return name; } public void setName(String name){ this.name = name; } @Override public String toString(){ return "Student: name='" + name + "'"; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj){ if (this == obj){ return true; } if (obj == null || getClass() != obj.getClass()){ return false; } Student student = (Student) obj; return name.equals(student.name); } @Override public int hashCode(){ return name.hashCode(); } }Python1.Math::random ()-> Math.random() 2.Math::sqrt (double number) -> Math.sqrt(number) 3. Student::getName (Student student)-> student.getName() 4. Student::setName (Student student,String name) -> student.setName(name) 5. Student::hashCode (Student student) -> student.hashCode() 6. Student::equals (Student student,Object obj) -> student.equals(o)假設已經有了對象 Student stu = new Student(“張三”)
- 對象已知的情況下,stu就不必要作爲參數進行傳遞了
- new 構造方法,在對象未知的情況下,調用的是無參構造;對象已知的情況下,調用的是有參構造
Python
1. stu::getName ()->stu.getName() 2. stu::setName (String name)-> stu.setName(name) 3. Student::new (String name) -> new Student(name)函數對象分類
如何分類
以下情況可以歸爲一類:
- 參數個數和類型相同
- 返回值類型相同
- 隻包含一個抽象方法(可以有很多其他方法)
- 可以使用注解@FunctionalInterface 來檢查
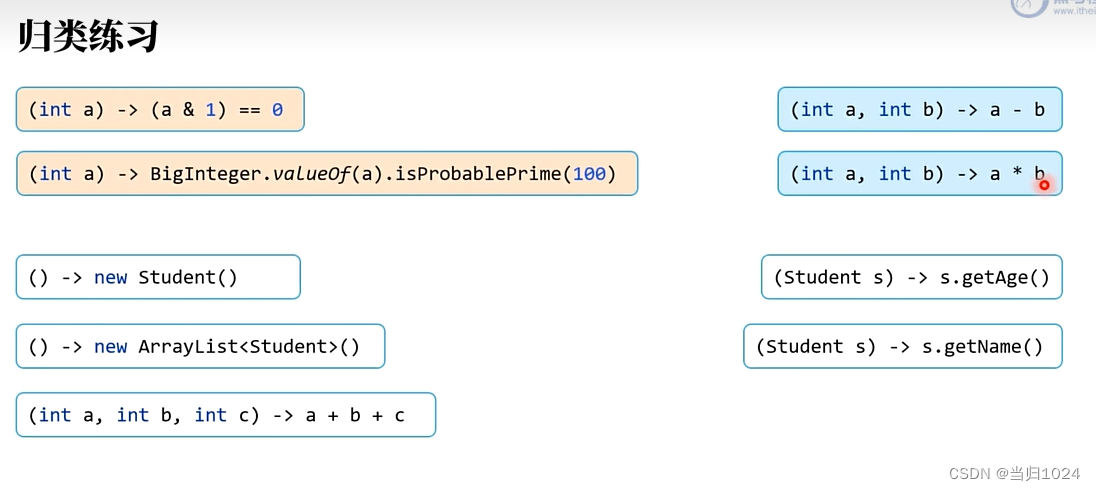
練習
 Python
Python// 判斷是是否是偶數 MyInterface1 type1 = (int a) -> (a & 1) == 0; // 可能是質數 MyInterface1 type2 = (int a) -> BigInteger.valueOf(a).isProbablePrime(100); // 函數式接口 有且僅有一個抽象方法 @FunctionalInterface interface MyInterface1{ boolean op(int arg1); }PythonMyInterface2 type3 = (int a, int b, int c) -> a + b + c; @FunctionalInterface interface MyInterface2{ int op(int num1, int num2, int num3); }PythonMyInterface3 type4 = (int a, int b) -> a + b; MyInterface3 type5 = (int a, int b) -> a * b; @FunctionalInterface interface MyInterface3{ int op(int num1, int num2); }Python// 即使函數式接口中的方法沒有攜帶參數,你也可以在方法體中攜帶參數 MyInterface4 type6 = () -> new Student("張三", 18); MyInterface5 type7 = () -> { List list = new ArrayList(); list.add(new Student("張三", 18)); list.add(new Student("李四", 19)); return list; }; // MyInterface5和MyInterface4是可以使用泛型合并的 MyInterface5_1 type6_1 = () -> new Student("張三", 18); MyInterface5_1 type7_1 = () -> { List list = new ArrayList(); list.add(new Student("張三", 18)); list.add(new Student("李四", 19)); return list; }; @FunctionalInterface interface MyInterface4{ Student op(); } @FunctionalInterface interface MyInterface5{ List op(); } // MyInterface5和MyInterface4是可以使用泛型合并的 @FunctionalInterface interface MyInterface5_1{PythonMyInterface6 type8 = (Student student) -> student.getName(); MyInterface7 type9 = (Student student) -> student.getage(); // MyInterface6和MyInterface7是可以使用泛型合并的 MyInterface8 type8_1 = (Student student) -> student.getName(); MyInterface8 type9_1 = (Student student) -> student.getage(); @FunctionalInterface interface MyInterface6{ String op(Student student) ; } @FunctionalInterface interface MyInterface7{ int op(Student student) ; } //MyInterface6和MyInterface7是可以使用泛型合并的 // O是返回值類型,I是入參類型 @FunctionalInterface interface MyInterface8{ O op(I inObj) ; }