原理简介~~
对于数据量较大的数据集,先对其中一部分图片打标签,Autolabelimg利用已标注好的图片进行训练,并利用训练得到的权重对其余数据进行自动标注,然后保存为xml文件。
一、下载yolov5v6.1
https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5
并对已标注的数据集进行训练,得到权重best.pt
二、将detect_auto.py文件放入yolov5根目录下
import sys
from utils.torch_utils import select_device
from models.common import DetectMultiBackend
from utils.datasets import *
import torch
from utils.general import (check_img_size, non_max_suppression, scale_coords)
from tkinter import *
from tkinter import filedialog
import natsort
# FILE = Path(__file__).resolve()
# ROOT = FILE.parents[0] # YOLOv5 root directory
# if str(ROOT) not in sys.path:
# sys.path.append(str(ROOT)) # add ROOT to PATH
# ROOT = Path(os.path.relpath(ROOT, Path.cwd())) # relative
import os
from os import getcwd
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET
class Detector():
def __init__(self):
self.objectList = []
self.weights = r"" # 可去官方下载v5 6.0的预训练权重模型
self.dnn = False
self.data = r"" # 选择你的配置文件(一般为.yaml)
self.device = select_device(device='0')
self.half = self.device.type != 'cpu' # 半精度化
self.predefined_classes = []
self.imgdir = r"" # 你需要标注的图片文件夹
self.outdir = r"" # 你需要保存的xml文件夹
self.detect_class = r"" # 你需要自动标注的类型
self.root_window = None
self.flag = False
@torch.no_grad()
def run(self,
frame,
model,
device,
half=False,
img_size=None,
augment=False,
visualize=False,
max_det=1000):
if img_size is None:
img_size = [640, 640]
img0 = frame
stride, names, pt, jit, onnx, engine = model.stride, model.names, model.pt, model.jit, model.onnx, model.engine
img_size = check_img_size(img_size, s=stride)
# Half
half &= (pt or jit or engine) and device.type != 'cpu' # half precision only supported by PyTorch on CUDA
if pt or jit:
model.model.half() if half else model.model.float()
img = letterbox(img0, auto=True, new_shape=img_size, stride=32)[0]
img = img.transpose((2, 0, 1))[::-1] # HWC to CHW, BGR to RGB
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
# model.warmup(imgsz=(1, 3, *img_size), half=half) # warmup
img = torch.from_numpy(img).to(device)
img = img.half() if half else img.float() # uint8 to fp16/32
img /= 255 # 0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0
if len(img.shape) == 3:
img = img[None] # expand for batch dim
pred = model(img, augment=augment, visualize=visualize)
pred = non_max_suppression(pred, max_det=max_det)
for i, det in enumerate(pred):
if det is not None and len(det):
det[:, :4] = scale_coords(img.shape[2:], det[:, :4], img0.shape).round()
info_list = []
for *xyxy, conf, cls in reversed(det):
xyxy = torch.tensor(xyxy).view(-1).tolist()
info = [xyxy[0], xyxy[1], xyxy[2], xyxy[3], int(cls)]
info_list.append(info)
return info_list
else:
return None
def create_annotation(self, xn):
global annotation
tree = ET.ElementTree()
tree.parse(xn)
annotation = tree.getroot()
# 遍历xml里面每个object的值如果相同就不插入
def traverse_object(self, AnotPath):
tree = ET.ElementTree(file=AnotPath)
root = tree.getroot()
ObjectSet = root.findall('object')
for Object in ObjectSet:
ObjName = Object.find('name').text
BndBox = Object.find('bndbox')
x1 = int(BndBox.find('xmin').text)
y1 = int(BndBox.find('ymin').text)
x2 = int(BndBox.find('xmax').text)
y2 = int(BndBox.find('ymax').text)
self.objectList.append([x1, y1, x2, y2, ObjName])
# 定义一个创建一级分支object的函数
def create_object(self, root, objl): # 参数依次,树根,xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax
# 创建一级分支object
_object = ET.SubElement(root, 'object')
# 创建二级分支
name = ET.SubElement(_object, 'name')
# print(obj_name)
name.text = str(objl[4])
pose = ET.SubElement(_object, 'pose')
pose.text = 'Unspecified'
truncated = ET.SubElement(_object, 'truncated')
truncated.text = '0'
difficult = ET.SubElement(_object, 'difficult')
difficult.text = '0'
# 创建bndbox
bndbox = ET.SubElement(_object, 'bndbox')
xmin = ET.SubElement(bndbox, 'xmin')
xmin.text = '%s' % objl[0]
ymin = ET.SubElement(bndbox, 'ymin')
ymin.text = '%s' % objl[1]
xmax = ET.SubElement(bndbox, 'xmax')
xmax.text = '%s' % objl[2]
ymax = ET.SubElement(bndbox, 'ymax')
ymax.text = '%s' % objl[3]
# 创建xml文件的函数
def create_tree(self, image_name, h, w, imgdir):
global annotation
# 创建树根annotation
annotation = ET.Element('annotation')
# 创建一级分支folder
folder = ET.SubElement(annotation, 'folder')
# 添加folder标签内容
folder.text = (imgdir)
# 创建一级分支filename
filename = ET.SubElement(annotation, 'filename')
filename.text = image_name
# 创建一级分支path
path = ET.SubElement(annotation, 'path')
# path.text = getcwd() + '\{}\{}'.format(imgdir, image_name) # 用于返回当前工作目录
path.text ='{}/{}'.format(imgdir, image_name) # 用于返回当前工作目录
# 创建一级分支source
source = ET.SubElement(annotation, 'source')
# 创建source下的二级分支database
database = ET.SubElement(source, 'database')
database.text = 'Unknown'
# 创建一级分支size
size = ET.SubElement(annotation, 'size')
# 创建size下的二级分支图像的宽、高及depth
width = ET.SubElement(size, 'width')
width.text = str(w)
height = ET.SubElement(size, 'height')
height.text = str(h)
depth = ET.SubElement(size, 'depth')
depth.text = '3'
# 创建一级分支segmented
segmented = ET.SubElement(annotation, 'segmented')
segmented.text = '0'
def pretty_xml(self, element, indent, newline, level=0): # elemnt为传进来的Elment类,参数indent用于缩进,newline用于换行
if element: # 判断element是否有子元素
if (element.text is None) or element.text.isspace(): # 如果element的text没有内容
element.text = newline + indent * (level + 1)
else:
element.text = newline + indent * (level + 1) + element.text.strip() + newline + indent * (level + 1)
# else: # 此处两行如果把注释去掉,Element的text也会另起一行
# element.text = newline + indent * (level + 1) + element.text.strip() + newline + indent * level
temp = list(element) # 将element转成list
for subelement in temp:
if temp.index(subelement) 0):
object_information = [int(coordinate[0]), int(coordinate[1]), int(coordinate[2]),
int(coordinate[3]), names[label_id]]
if (self.objectList.count(object_information) == 0):
self.create_object(annotation, object_information)
self.objectList = []
# 将树模型写入xml文件
tree = ET.ElementTree(annotation)
root = tree.getroot()
self.pretty_xml(root, '\t', '\n')
# tree.write('.\{}\{}.xml'.format(outdir, image_name.strip('.jpg')), encoding='utf-8')
tree.write('{}\{}.xml'.format(self.outdir, image_name.strip(file_tail)), encoding='utf-8')
else:
print(image_name)
# 客户端
def client(self):
def creatWindow():
self.root_window.destroy()
window()
def judge(str):
if (str):
text = "你已选择" + str
else:
text = "你还未选择文件夹,请选择"
return text
def test01():
self.imgdir = r""
self.imgdir += filedialog.askdirectory()
creatWindow()
def test02():
self.outdir = r""
self.outdir += filedialog.askdirectory()
creatWindow()
def test03():
self.data = r""
self.data += filedialog.askopenfilename()
creatWindow()
def test04():
self.weights = r""
self.weights += filedialog.askopenfilename()
creatWindow()
def test05():
self.detect_class = r""
self.detect_class += filedialog.askopenfilename()
creatWindow()
def tes06():
self.work()
self.flag=True
creatWindow()
def window():
self.root_window = Tk()
self.root_window.title("")
screenWidth = self.root_window.winfo_screenwidth() # 获取显示区域的宽度
screenHeight = self.root_window.winfo_screenheight() # 获取显示区域的高度
tk_width = 500 # 设定窗口宽度
tk_height = 400 # 设定窗口高度
tk_left = int((screenWidth - tk_width) / 2)
tk_top = int((screenHeight - tk_width) / 2)
self.root_window.geometry('%dx%d+%d+%d' % (tk_width, tk_height, tk_left, tk_top))
self.root_window.minsize(tk_width, tk_height) # 最小尺寸
self.root_window.maxsize(tk_width, tk_height) # 最大尺寸
self.root_window.resizable(width=False, height=False)
btn_1 = Button(self.root_window, text='请选择你要标注的图片文件夹', command=test01,
height=0)
btn_1.place(x=169, y=40, anchor='w')
text = judge(self.imgdir)
text_label = Label(self.root_window, text=text)
text_label.place(x=160, y=70, anchor='w')
btn_2 = Button(self.root_window, text='请选择你要保存的xml文件夹(.xml)', command=test02,
height=0)
btn_2.place(x=169, y=100, anchor='w')
text = judge(self.outdir)
text_label = Label(self.root_window, text=text)
text_label.place(x=160, y=130, anchor='w')
btn_3 = Button(self.root_window, text='请选择你的配置文件(.yaml)', command=test03,
height=0)
btn_3.place(x=169, y=160, anchor='w')
text = judge(self.data)
text_label = Label(self.root_window, text=text)
text_label.place(x=160, y=190, anchor='w')
# if(self.outdir and self.imgdir and self.data):
btn_4 = Button(self.root_window, text='请选择使用的模型(.pt)', command=test04,
height=0)
btn_4.place(x=169, y=220, anchor='w')
text = judge(self.weights)
text_label = Label(self.root_window, text=text)
text_label.place(x=160, y=250, anchor='w')
btn_5 = Button(self.root_window, text='请选择需要自动标注的类别文件(.txt)', command=test05,
height=0)
btn_5.place(x=169, y=280, anchor='w')
text = judge(self.detect_class)
text_label = Label(self.root_window, text=text)
text_label.place(x=160, y=310, anchor='w')
btn_6 = Button(self.root_window, text='开始自动标注', command=tes06,
height=0)
btn_6.place(x=169, y=340, anchor='w')
if (self.flag):
text = "标注完成"
else:
text = "等待标注"
text_label = Label(self.root_window, text=text)
text_label.place(x=160, y=370, anchor='w')
self.root_window.mainloop()
window()
if __name__ == '__main__':
detector = Detector()
detector.client()
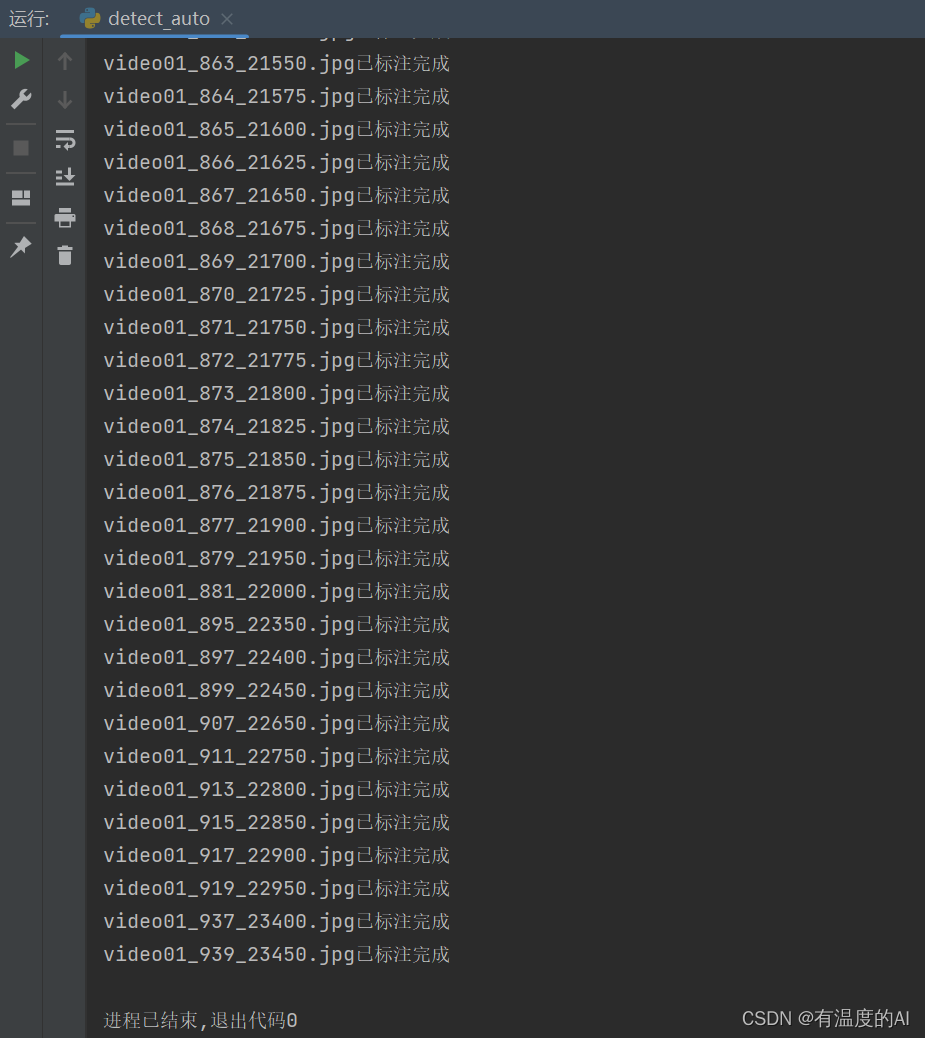
三、运行detect_auto.py文件
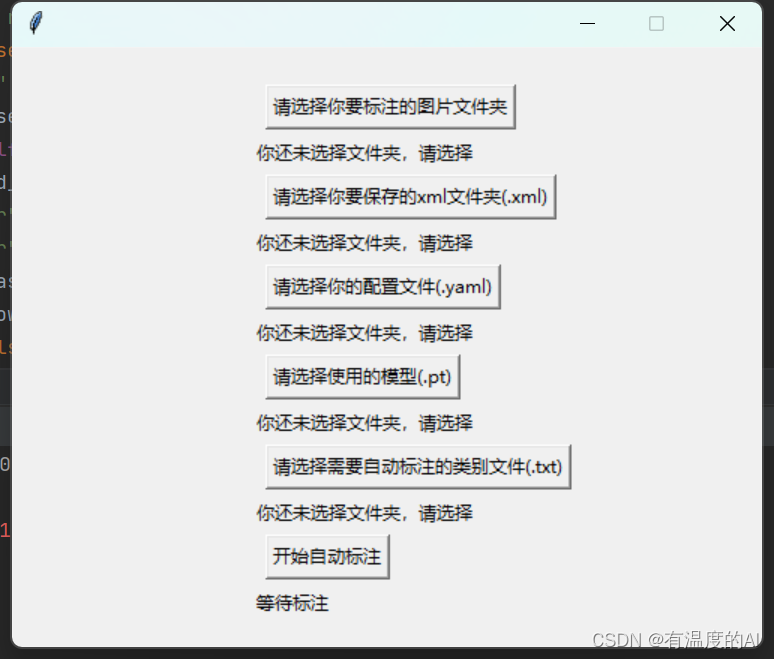
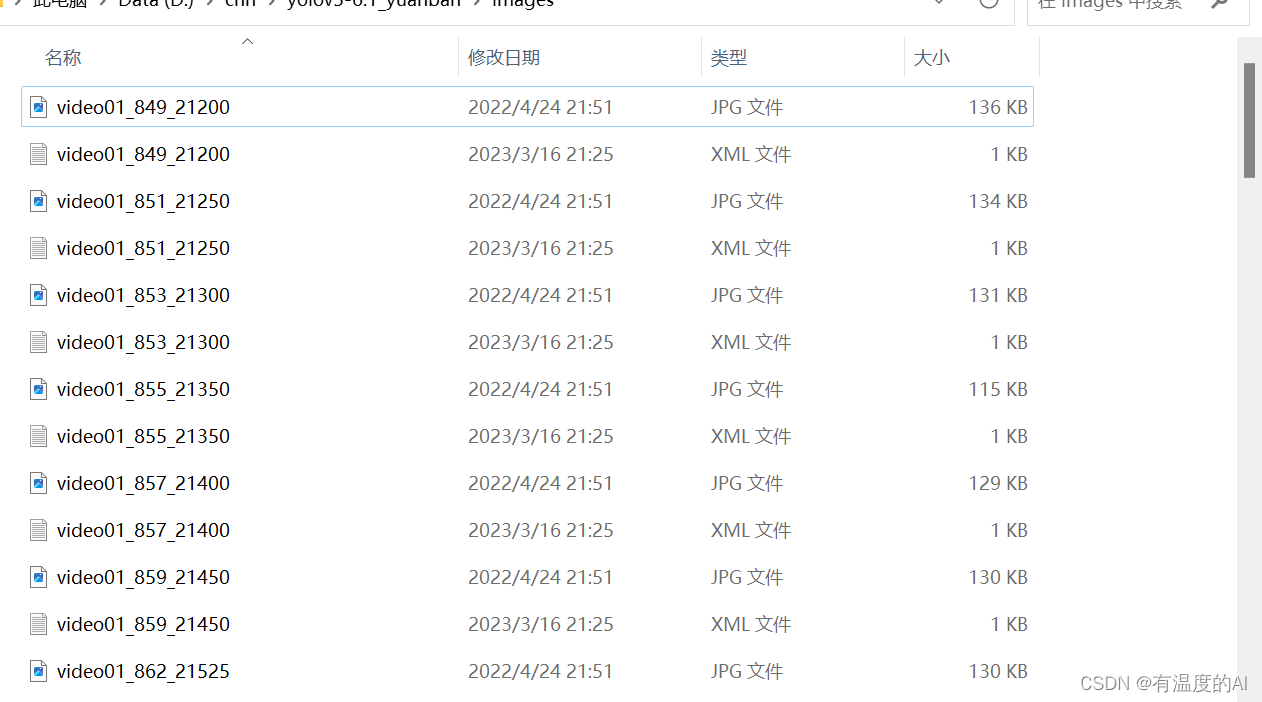
- 建议将要标注的图片文件和标注完的.xml文件放在同一文件夹下,这样方便使用labelimg查看标注效果;
- 配置文件即为训练时data文件夹下对应的.yaml文件;
- 使用的模型为训练好的权重文件(best.pt);
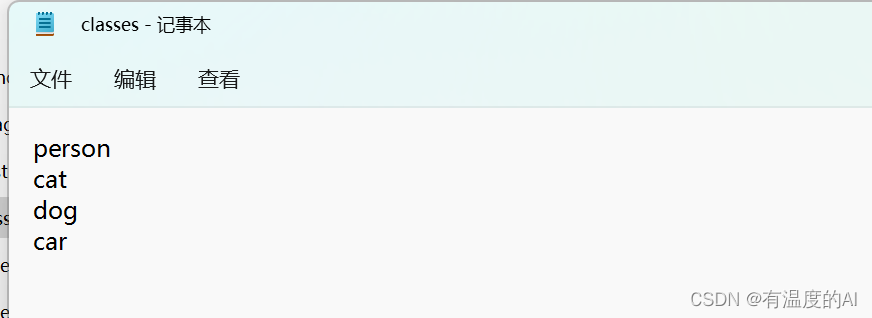
- 在根目录下创建class.txt文件,里面为数据集所包含的类别;