一 简介:
TensorRT是一个高性能的深度学习推理(Inference)优化器,可以为深度学习应用提供低延迟、高吞吐率的部署推理。TensorRT可用于对超大规模数据中心、嵌入式平台或自动驾驶平台进行推理加速。TensorRT现已能支持TensorFlow、Caffe、Mxnet、Pytorch等几乎所有的深度学习框架,将TensorRT和NVIDIA的GPU结合起来,能在几乎所有的框架中进行快速和高效的部署推理。
在平时的工作与学习中也都尝试过使用Libtorch和onnxruntime的方式部署过深度学习模型。但这两款多多少少存在着内存与显存占用的问题,并且无法完全释放。(下文的部署方式不仅简单并且在前向推理过程所需的显存更低,并且在推理结束后可以随时完全释放显存)。
二 安装:
1.安装环境
win10
vs2019
cuda10.2
pytorch1.9
只要其中的pytorch,cuda版本与后续的Tensorrt版本对应即可
2.模型转化
首先需要将pytorch的.pth模型转化为onnx的模型(为了后边的方便,目前讲解的方式都是单卡的方式)。转化方式很简单pytorch已经提供,网上也有许多讲解这个函数的博客。此处直接上代码:(必须确定.pth模型是可以正常使用的否则后面转化的模型也都无法使用)。
def Convert_ONNX(model,input_size):
model.eval()
dummy_input = torch.randn(input_size).cuda()
torch.onnx.export(model, # model being run
dummy_input, # model input (or a tuple for multiple inputs)
"PytorchtoOnnx.onnx", # where to save the model
# dynamic_axes = {'inputs':{0:"batch"}}, #表示batch这个维度可变的 (有这个参数可以关闭不用设置)会麻烦很多
verbose = True,
export_params=True, # store the trained parameter weights inside the model file
input_names = ['inputs'], # the model's input names
output_names = ['modelOutput']) # the model's output names
print("end")
3.将onnx模型通过tensorrt自带工具完成转化
首先去官网https://developer.nvidia.com/nvidia-tensorrt-download下载与自己pytorch版本和cuda版本适应的tensorrt版本。
下载完成后打开里面的bin文件夹,里面存在着一个trtexec.exe。利用以下代码将之前获得的onnx文件转化为trt文件。这里讲解最简单的方式,因为trtexec.exe有许多可以优化的功能,最终都会影响模型的精度与速度。在命令行中输入如下指令。
trtexec.exe --onnx=PytorchtoOnnx.onnx --saveEngine=TrtModel.trt --explicitBatch --workspace=4096
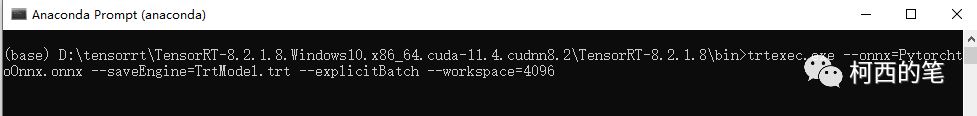
这里模型转化可能需要一点时间,完成转化后会得到TrtMedel.trt模型。那么准备工作也就完成了。接下来开始C++部署。
三 部署:
1.打开VS新建空项目
2.配置环境
在VC++目录---包含目录中添加cuda路径和tensorrt路径(此处用的是相对路径,你也可以用绝对路径)其中$(CUDA_PATH)\include是指cuda中的include文件,我的在C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v10.2\include
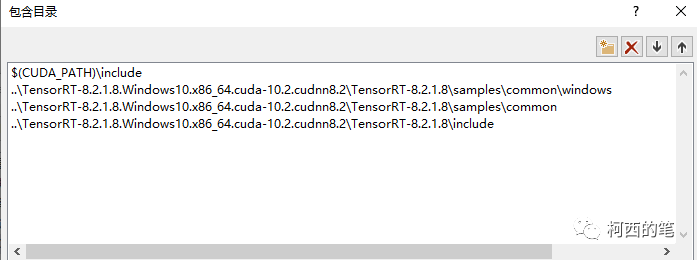
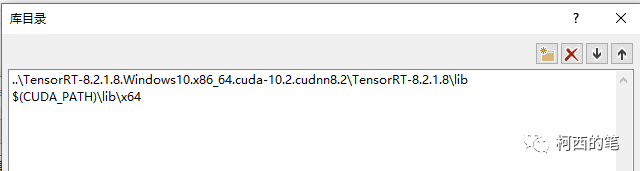
在VC++目录---库目录中添加
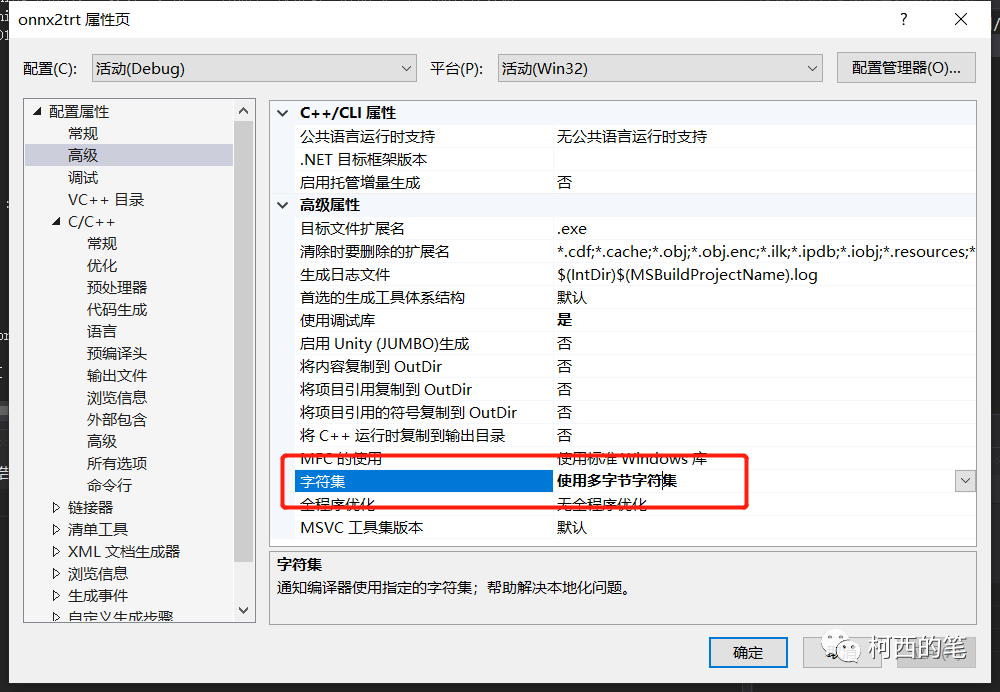
还需要将字符集改成:使用多字节字符集。否则会报C2664 “HMODULE LoadLibraryW(LPCWSTR)”: 无法将参数 1 从“const _Elem *”转换为“LPCWSTR” 的错误。
3.部署代码
必须新建一个logger.cpp的文件。里面写入如下代码。
#include "logger.h"
#include "ErrorRecorder.h"
#include "logging.h"
SampleErrorRecorder gRecorder;
namespace sample
{
Logger gLogger{Logger::Severity::kINFO};
LogStreamConsumer gLogVerbose{LOG_VERBOSE(gLogger)};
LogStreamConsumer gLogInfo{LOG_INFO(gLogger)};
LogStreamConsumer gLogWarning{LOG_WARN(gLogger)};
LogStreamConsumer gLogError{LOG_ERROR(gLogger)};
LogStreamConsumer gLogFatal{LOG_FATAL(gLogger)};
void setReportableSeverity(Logger::Severity severity)
{
gLogger.setReportableSeverity(severity);
gLogVerbose.setReportableSeverity(severity);
gLogInfo.setReportableSeverity(severity);
gLogWarning.setReportableSeverity(severity);
gLogError.setReportableSeverity(severity);
gLogFatal.setReportableSeverity(severity);
}
} // namespace sample
再新建一个test.cpp进行测试。测试代码如下:(下面是一个unet的分割模型,并且前面的预处理例如标准化等都在外面完成了。下面只涉及到推理部分)。
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#include
#include "NvInfer.h"
#include "argsParser.h"
#include "logger.h"
#include "common.h"
#include "NvOnnxParser.h"
#include "buffers.h"
using namespace nvinfer1;
bool read_TRT_File(const std::string& engineFile, ICudaEngine*& engine)
{
fstream file;
file.open(engineFile, ios::binary | ios::in);
file.seekg(0, ios::end); // 定位到 fileObject 的末尾
int length = file.tellg();
file.seekg(0, std::ios::beg); // 定位到 fileObject 的开头
unique_ptr data(new char[length]);
file.read(data.get(), length);
file.close();
nvinfer1::IRuntime* trtRuntime = createInferRuntime(sample::gLogger.getTRTLogger());
engine = trtRuntime->deserializeCudaEngine(data.get(), length, nullptr);
assert(engine != nullptr);
std::cout destroy();
return true;
}
void doInference(IExecutionContext& context, float* input, float* output,int InputSize, int OutPutSize,int BatchSize)
{
const char* INPUT_BLOB_NAME = "inputs";
const char* OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME = "modelOutput";
const ICudaEngine& engine = context.getEngine();
// input and output buffer pointers that we pass to the engine - the engine requires exactly IEngine::getNbBindings(),
// of these, but in this case we know that there is exactly one input and one output.
assert(engine.getNbBindings() == 2);
void* buffers[2];
// In order to bind the buffers, we need to know the names of the input and output tensors.
// note that indices are guaranteed to be less than IEngine::getNbBindings()
const int inputIndex = engine.getBindingIndex(INPUT_BLOB_NAME);
const int outputIndex = engine.getBindingIndex(OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME);
// DebugP(inputIndex); DebugP(outputIndex);
// create GPU buffers and a stream
CHECK(cudaMalloc(&buffers[inputIndex], InputSize * sizeof(float)));
CHECK(cudaMalloc(&buffers[outputIndex], OutPutSize * sizeof(float)));
cudaStream_t stream;
CHECK(cudaStreamCreate(&stream));
// DMA the input to the GPU, execute the batch asynchronously, and DMA it back:
CHECK(cudaMemcpyAsync(buffers[inputIndex], input, InputSize * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, stream));
context.enqueue(BatchSize, buffers, stream, nullptr);
CHECK(cudaMemcpyAsync(output, buffers[outputIndex], OutPutSize * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, stream));
cudaStreamSynchronize(stream);
// release the stream and the buffers
cudaStreamDestroy(stream);
CHECK(cudaFree(buffers[inputIndex]));
CHECK(cudaFree(buffers[outputIndex]));
}
void runs(short* Data, int ImageCol, int ImageRow, int ImageLayer, unsigned char* Outputs)
{
int numall = ImageCol * ImageRow * ImageLayer;
float* PatchData = new float[numall];
Process(Data, ImageCol, ImageRow, ImageLayer, PatchData); //前处理
string eigineFile = "TrtMedel.trt";
ICudaEngine* engine = nullptr;
read_TRT_File(eigineFile, engine);
IExecutionContext* context = engine->createExecutionContext();
assert(context != nullptr);
float* out_image = new float[3 * numall];
int batchsize = 1;
int InputSize = 1 * 1 * numall;
int OutputSize = 1 * 3 * numall;
doInference(*context, PatchData, out_image, InputSize, OutputSize, batchsize);
EndProcess(out_image, 3, ImageCol, ImageRow, ImageLayer, Outputs); //后处理
context->destroy();
engine->destroy();
cudaDeviceReset();
delete[] out_image;
delete[] PatchData;
cout