目录
- 1.链表和顺序表优缺点
- 2.栈
- 栈的概念及结构
- 实现栈的方式:数组栈
- 3.队列
- 队列的概念及结构
- 队列的实现:链式队列
1.链表和顺序表优缺点
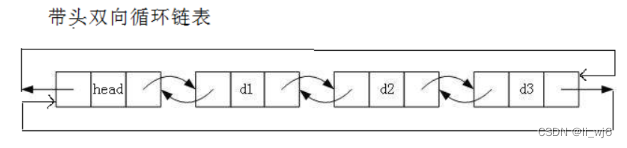
链表
优点:1.带头双向循环链表可在任意位置插入删除节点O(1)。2.按需申请释放空间。
缺点:1.不支持下标随机访问。2.CPU高速缓存命中率会更低。
顺序表
优点:1.尾插尾删效率较高。2.下标随机访问。3.CPU高速缓存命中率会更高。
缺点:1.前面部分插入删除数据,效率是O(N),需要挪动数据。2.空间不够,需要扩容。(扩容是需要付出代价的、一般还会伴随空间的浪费)。
2.栈
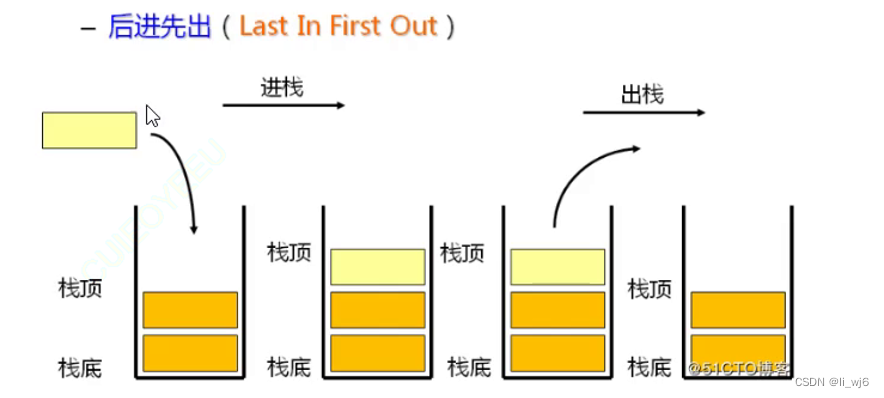
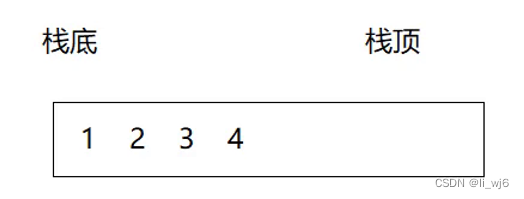
栈的概念及结构

实现栈的方式:数组栈
下面用一个动态数组来模拟栈(顺序表)。
//需要用到的头文件 #include #include #include #include
typedef int STDataType; typedef struct Stack { STDataType* a; int top;//栈顶元素 int capacity;//栈空间 }ST;//用顺序表来模拟栈//初始化栈 void STInit(ST* pst) { assert(pst); pst->a = NULL; //下面有两种方式来定义top //pst->top = -1; //top 指向栈顶数据 pst->top = 0;//top 指向栈顶数据的下一个位置 pst->capacity = 0; }//销毁栈 void STDestroy(ST* pst) { asserta(pst); free(pst->a); pst->a = NULL; pst->top = pst->capacity = 0; }//栈顶插入数据 void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x) { if (pst->top == pst->capacity)//扩容 { int newCapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2; STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, newCapacity*sizeof(STDataType)); if (tmp == NULL) { perror("realloc fail"); return; } pst->a = tmp; pst->capacity = newCapacity; } pst->a[pst->top] = x; pst->top++; }//栈顶出数据 void STPop(ST* pst) { assert(pst); assert(!STEmpty(pst));//栈不为空再进行删除 pst->top--; }//获取栈顶元素 STDataType STTop(ST* pst) { assert(pst); assert(!STEmpty(pst));//栈不为空再获取 return pst->a[pst->top - 1]; }//探空 bool STEmpty(ST* pst) { assert(pst); return pst->top == 0; }//获取size int STSize(ST* pst) { assert(pst); return pst->top; }3.队列
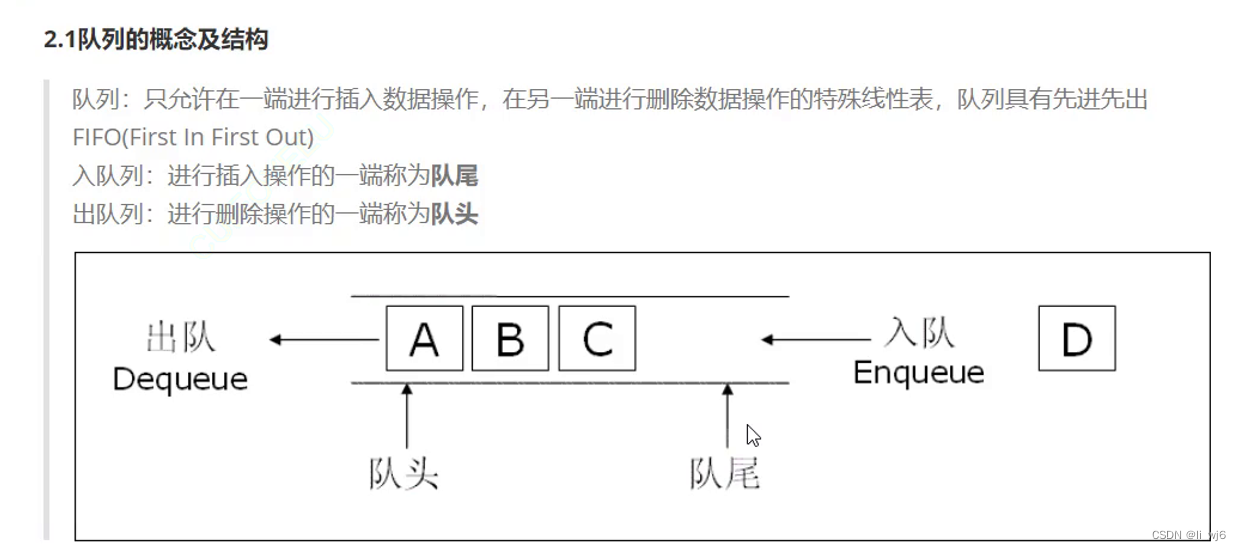
队列的概念及结构
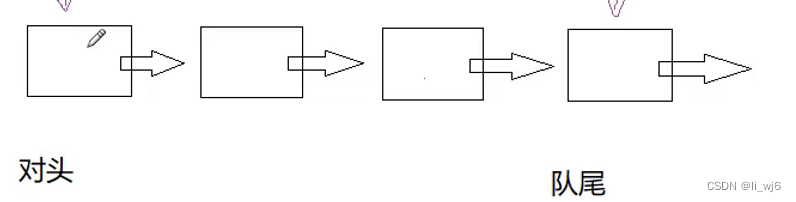
队列的实现:链式队列
//需要用到的头文件 #include #include #include #include
typedef int QDataType; typedef struct QueueNode { struct QueueNode* next; QDataType data; }QNode;//定义节点 typedef struct Queue { QNode* phead; QNode* ptail; int size; }Queue;//队列初始化 void QueueTnit(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); pq->phead = NULL; pq->ptail = NULL; pq->size = 0; }//队列销毁 void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); QNode* cur = pq->phead; while (cur) { QNode* next = cur->next; free(cur); cur = next; } pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL; pq->size = 0; }//数据从队尾入队列 void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x) { assert(pq); QNode* newNode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode*)); if (newNode == NULL) { perror("malloc fail\n"); return; } newNode->data = x; newNode->next == NULL; if (pq->ptail == NULL) { assret(pq->phead == NULL); pq->phead = newNode; } else { pq->ptail->next = newNode; pq->ptail = newNode; pq->size++; } }//数据从对头出队列 void QueuePop(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); //一个节点和多个节点 if (pq->phead->next == NULL)//只有一个节点 { free(pq->ptail); pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL; } else//有多个节点 { QNode* next = pq->phead->next; free(pq->phead); pq->phead = next; } pq->size--; }//取对头数据 QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); return pq->phead->data; }//取队尾数据 QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); return pq->ptail->data; }//取队列数据个数 int QueueSize(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); return pq->size; }//判断队列是否为空 bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); return pq->phead == NULL && pq->ptail == NULL; }