hashmap
- 1、hashmap 与 hashtable 的区别
- 2、hashmap
- 基本类型与包装类
- 常用实现
- 变量介绍
- HashMap的内部变量:
- 初始容量和负载因子
- 红黑树和链表转化
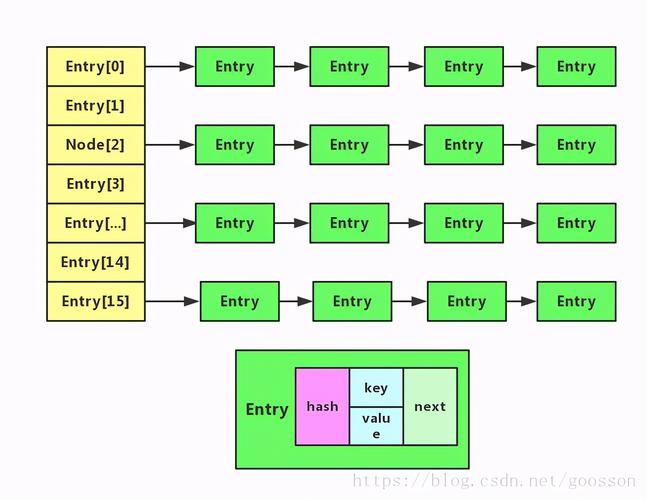
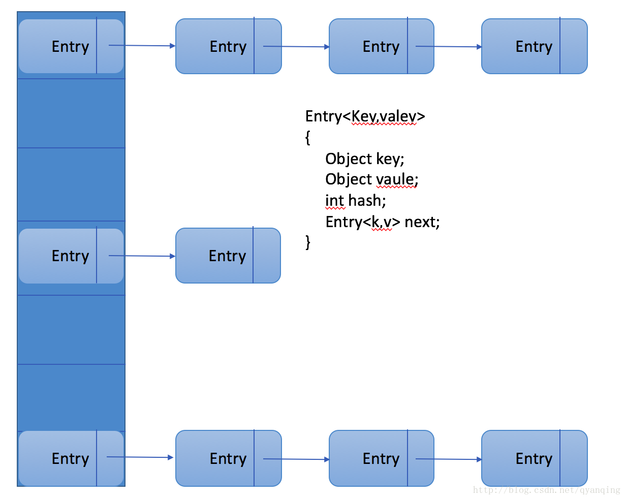
- HashMap的内部数据结构
- HashMap内部哈希算法
- 参考文章
1、hashmap 与 hashtable 的区别
- 线程安全
- null值
- 执行效率
2、hashmap
hashmap是java中常用的集合类之一,
 (图片来源网络,侵删)
(图片来源网络,侵删)- 继承自AbstractMap类,实现了 Map、Cloneable、java.io.Serializable 接口。
- 使用哈希表来存储键值对(key-value),通过将键值映射成哈希码来进行高效的插入、删除操作。
- 具有很快的访问速度,最多允许一条记录的键为 null,不支持线程同步。
java.lang.Object java.util.AbstractMap java.util.HashMap Type Parameters: K - the type of keys maintained by this map V - the type of mapped values All Implemented Interfaces: Serializable, Cloneable, Map Direct Known Subclasses: LinkedHashMap, PrinterStateReasons public class HashMap extends AbstractMap implements Map, Cloneable, Serializable
基本类型与包装类
HashMap 中的元素实际上是对象,一些常见的基本类型可以使用它的包装类。
基本类型对应的包装类表如下:
 (图片来源网络,侵删)
(图片来源网络,侵删)基本类型 引用类型 boolean Boolean byte Byte short Short int Integer long Long float Float double Double char Character 常用实现
1、创建
import java.util.HashMap; // 引入 HashMap 类 HashMap A = new HashMap();
2、添加元素 put() 方法:
当调用put方法的时候,先通过hashCode() 获取key 的hashCode,然后找到bucket位置,将Entry对象 存储到bucket上面。
public class Test { public static void main(Strings[] args) { // 创建 HashMap 对象 A HashMap A = new HashMap(); // 添加键值对 A.put(1, "apple"); A.put(2, "banana"); System.out.println(A); } }3、访问元素 get(key) 方法:
通过get(key)获取对象时,也是通过hashCode()方法 获取key的hashCode,然后得到Entry对象。
public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建 HashMap 对象 A HashMap A = new HashMap(); // 添加键值对 A.put(1, "apple"); A.put(2, "banana"); // 访问 System.out.println(A.get(1)); } }4、删除元素 remove(key)方法:
public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建 HashMap 对象 A HashMap A = new HashMap(); // 添加键值对 A.put(1, "apple"); A.put(2, "banana"); // 删除 A.remove(1); } }5、删除所有元素 clear()方法
6、计算 HashMap 中元素的数量 size() 方法
7、 遍历
- 可以使用 for-each 来迭代 HashMap 中的元素
- 只想获得 key ,使用 KeySet() 方法,然后通过 get(key) 获取对应的 value
- 指向获得value,有getValue() 方法.
// 方法一: Iterator iterator = hashMap.keySet().iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()){ String key = (String)iterator.next(); System.out.println(key+"="+hashMap.get(key)); } // 方法二: Iterator iterator1 = hashMap.entrySet().iterator(); while (iterator1.hasNext()){ Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) iterator1.next(); String key = (String) entry.getKey(); Integer value = (Integer) entry.getValue(); System.out.println(key+"="+value); }变量介绍
该类提供了四种构造方法:
(1)HashMap()
Constructs an empty HashMap with the default initial capacity (16) and the default load factor (0.75).
public HashMap(){ this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; //all other fields defaulted }这是我们用的比较频繁的一个构造方法了,没有特殊的写法,所有变量均是默认值
(2) HashMap(int initialCapacity)
Constructs an empty HashMap with the specified initial capacity and the default load factor (0.75).
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) { this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR); }该构造方法传入一个指定容量,然后调用另外一个重载的构造方法
(3) HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor)
Constructs an empty HashMap with the specified initial capacity and load factor.
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { if(initialCapacity MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; if(loadFactor